Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Sacrifi ce the animal after 20 s, collect the brain, and quickly
●
freeze in prechilled 2-methylbutane at −45°C. The specimens
can be stored at −80°C till needed.
Cut coronal sections (20-
μ
m thick) of the whole brain in a
●
cryostat
Place brain sections in X-ray cassettes and expose onto X-ray
●
fi lms for 8 days
Develop fi lm according to standard methods
●
5.2. Laser Doppler
Flowmetry
One of the simplest methods for measuring CBF is noninvasive Laser
Doppler Flowmetry (LDF). The initial investment is relatively
expensive but the technique is easy to use with minimal training or
technical knowledge. LDF has been validated by comparison with
autoradiography (
42
) and microspheres (
43
). By scanning the
desired area with a laser beam, colored images are created (with a
spatial resolution of ~1 mm and temporal resolution of 200 ms).
The intensity of blood fl ow is refl ected by the different colors
(Fig.
2
). This technique is very useful to monitor changes in the
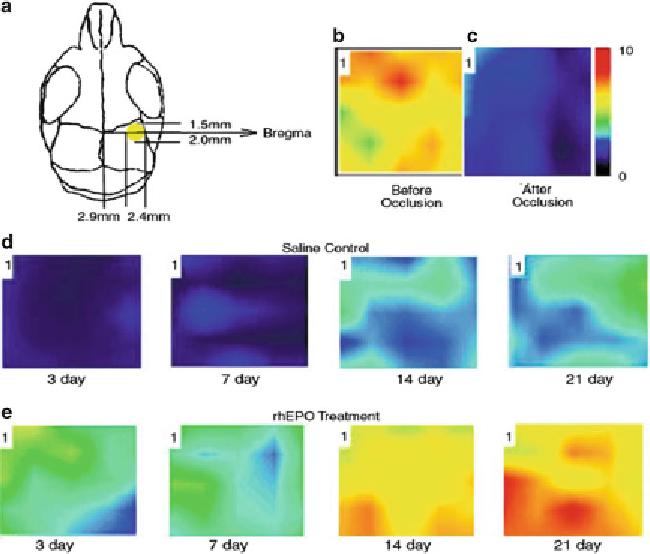
Fig. 2. Blood fl ow measurements using the Laser Doppler Flowmetry method to test the effects of rhEPO treatment in the
ischemic brain. (
a
) The scanning region is defi ned by the ischemic core (
yellow area
) and penumbra regions in the ipsilat-
eral cortex. (
b
,
c
) Laser scanning images before and immediately after MCA-common carotid artery occlusion showing a
signifi cant reduction of blood fl ow after occlusion. (
d
,
e
) Laser scanning images of LCBF in stroke region 3-21 days after
the ischemic insult in a saline control mouse (
d
) and a rhEPO-treated mouse (
e
). Marked LCBF recovery can be seen
14 days after the onset of ischemia in the rhEPO-treated brain. Adapted from ref. (
45
) .
Search WWH ::

Custom Search