Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
18
x
10
4
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
−10
−5
0
5
10
Sample bin
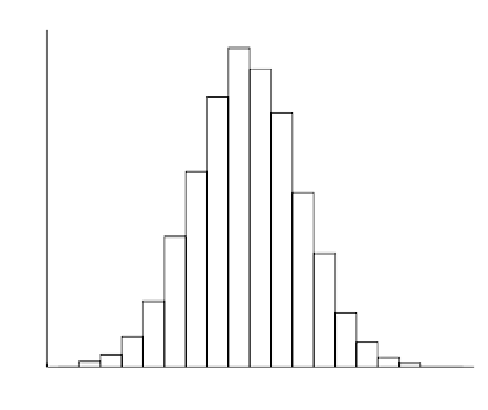
FIGURE 4.5. Histogram of 1,048,576 data samples.
accomplish this for most ADCs there are three basis functions which must be ac-
complished. These are
amplification
,
frequency translation/downconversion
,and
filtering
. These prepare the signal for analog-to-digital conversion, which results
in the samples to be processed within the software receiver.
4.3
Resulting Sampled Data
Now that the operation/functionality of the GNSS front end has been described,
it is worthwhile to highlight the resulting data that have been collected from the
front-end design depicted in Figure 4.2 and have been included on the media with
the topic.
Again, the important parameters for the signal processing are
-
Sampling frequency: 38
192 MHz
-
Intermediate frequency: 9
.
.
548 MHz, and
-
Four-bit samples.
The above parameters provide all the necessary information for the operation
of the signal processing algorithms. Some other items, such as the time and date
and approximate location of the data collection, can speed the acquisition as will
be discussed, but are not required.
What can be done is to show the resulting digital samples in typical representa-
tions. Thus, in Figures 4.4, 4.5, and 4.6, a time domain, histogram, and frequency
domain depiction of the collected data are illustrated, respectively.
In the time domain depiction, no discernable structure is visible despite the
9
548 MHz IF for the collected GPS data. In the histogram, it is obvious that all
four bits of the ADC are being triggered based on the 16 levels present within
.












Search WWH ::

Custom Search