Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
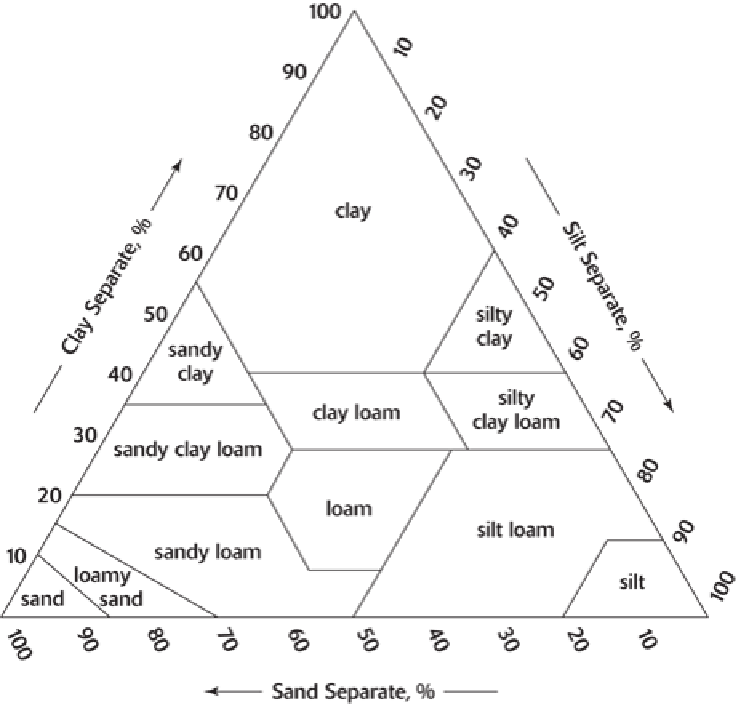
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture
Figure C-5:
Soil texture triangle.
Solar Cooker/Solar House
This activity allows for creativity and innovation while designing a solar house or solar cooker that uses the
sun's rays to magnify and/or trap heat. Lab objectives include defining the difference between active and pass-
ive solar energy, learning how both can be utilized, and discovering how to identify the important components
of each. Active solar power uses the sun's radiation as energy to power electrical or mechanical equipment
(equipment that moves). Passive solar power does not use another energy source or active mechanical systems.
Active systems use fans, pumps, and other technology, while passive systems are simple and have minimal
moving parts.
Specific Heat: Solar Absorption
With the increasing use of solar energy, it is important to understand how this energy is best captured. All sub-
stances absorb heat, and their capacity to do so is called their "specific heat." Specific heat is the amount of
heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C. Different materials have different specif-