Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
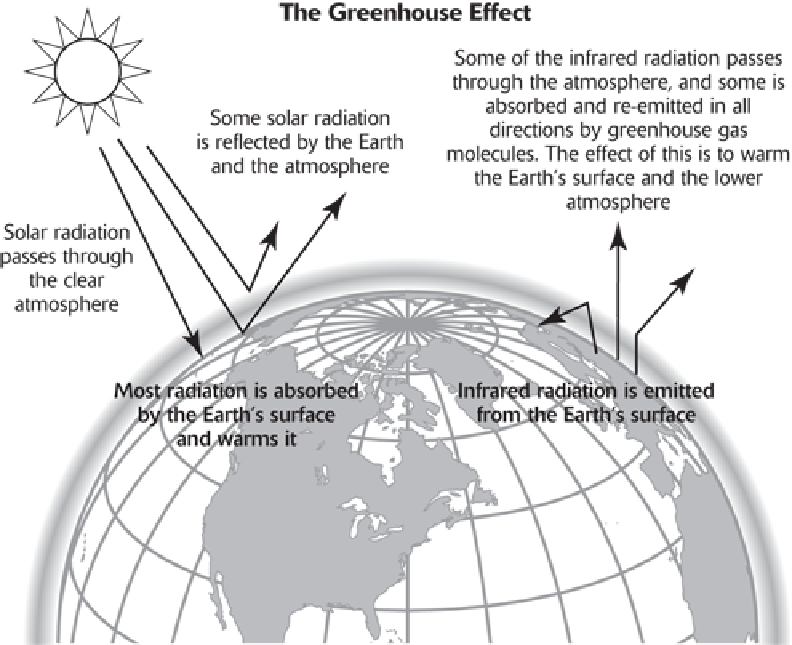
Source: Environmental Protection Agency
Other gases found naturally in the atmosphere also are considered greenhouse gases, insulating and acting as
positive factors in the atmosphere in moderate concentrations and having a negative impact at increasing con-
centrations. Here are some of the most prominent of the greenhouse gases:
•
Carbon dioxide (CO
2
)
is the most prominent greenhouse gas in the Earth's atmosphere. The primary
sources of CO
2
are the burning of fossil fuels, decomposition, deforestation, and cellular respiration.
This means that burning fires, motor vehicles, and smokestacks of factories that burns coal all emit car-
bon dioxide. Without carbon dioxide in the air, the Earth would be very cold. Carbon dioxide can spend
an average of 50 to 100 years (or more) in the troposphere.
•
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl
4
)
was primarily used in the production of cleaning fluids, especially in the
manufacture of military airplanes and spacecrafts. It has an average time in the troposphere of about 50
years.
•
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
spend a relatively short 15 years in the troposphere but a much longer
time in the stratosphere, where they damage ozone (as previously discussed). Historically, the primary
sources of CFCs included coolants used in air conditioners and refrigerators, foam and insulation pro-
duction, and aerosol spray cans. For the most part, these sources have been eliminated or are in the pro-
cess of being eliminated.