Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
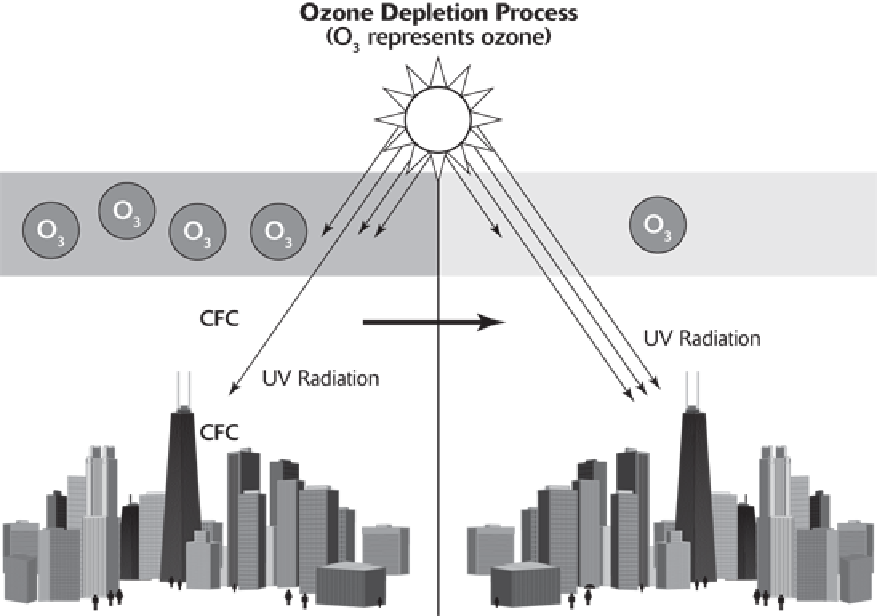
Environmental Effects of Ozone Depletion
Ozone depletion and the resulting increase in ultraviolet radiation harm the Earth, humans, plants, and animals.
Some of these adverse effects include the following:
• Changes in weather patterns
• Increased cooling of the stratosphere and warming of the troposphere due to less ozone to absorb the UV
radiation, allowing more to reach the Earth's surface
• Increased formation of ground-level smog
• Increased damage to the skin (for example, sunburns)
• Increased UV radiation (UVB), which plays a major role in malignant melanoma skin cancer
• Increase of eye diseases (for example, cataracts)
• Increased damage to plants (including hardwood forests)
• Increased damage to agricultural crops, reducing food availability
• Increased harmful effects on animals, which may threaten the extinction of some species
• Disruption of productivity of ecosystem food chains, such as reduced growth of phytoplankton (tiny
floating algae in the ocean, which are the base of the marine food chain)
• Weakening the efficiency of humans immune system
• Increased rate of mutations in human and nonhuman DNA, which are damaged by UVB radiation