Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Solar
The sun's radiant energy is used both to create heat directly and for conversion into electrical energy. There are
two types of systems:
•
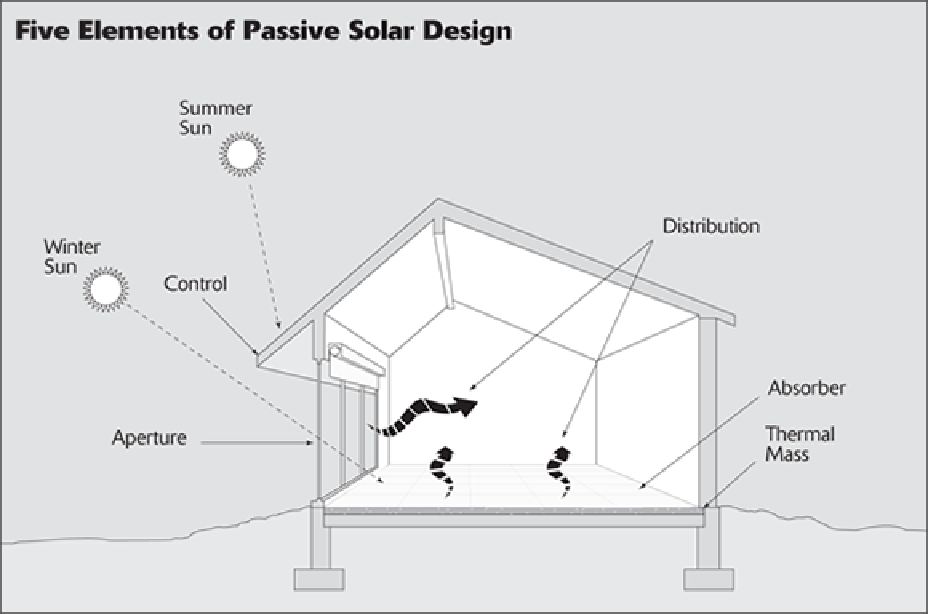
Passive solar energy systems
require no moving parts and, thus, no input of electrical activity. These in-
clude both gravity-fed heating systems and photovoltaic cells, which capture the sun's energy to generate
electricity. In a solar electricity system, sunlight hits the transparent solar cells causing them to emit
electrons, and many cells wired together produce electricity. The electricity can be used immediately,
cells can be connected to batteries to store the energy for later use, or cells can be connected to the
power grid to share electricity with other users. Detractors point to the inefficiency of solar cells, but
newer photovoltaic cells have increased this efficiency.
Additional passive heating systems include the use of materials that allow the heat from the sun to be
captured in the winter and reflected in the summer. Generally, these buildings are constructed to face
the primary direction of the sun, maximizing the potential to trap heat in the winter.
•
Active solar energy systems
use pumps and fans to move water heated by the sun throughout buildings,
requiring some input of electrical energy. This hot water can be used to heat the house and can be used
as hot water for cleaning and bathing.
See the following figures for illustrations of passive and active solar energy.