Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Buses are the most commonly used form of mass transit, partly because they can easily adjust their routes and
time schedules to meet the needs of the population they serve. As transit systems have replaced their aging
buses, they often choose buses that run on compressed natural gas (CNG). CNG burns cleaner than diesel, re-
ducing CO
2
and particulates emissions. Bus systems offer low fares to attract riders, often operating at a loss
and, thus, must rely on governments to subsidize their expenses.
Some cities have subway systems, most of which are underground electric light-rail systems. Chicago and a
few other cities have elevated systems. One distinction between buses and subways is that subway systems are
removed from the flow of traffic and, thus, can provide a faster form of transportation when city streets are
clogged. Subways use less energy and generate less pollution than cars, require less land for tracks and park-
ing, cause fewer accidents and deaths than cars, and reduce congestion in the cities. Disadvantages include a
fixed track system that cannot be adjusted to meet changes in society, the cost of building and maintenance,
and the noise and vibrations can impact nearby residents and businesses.
Light-rail systems are usually powered by electricity but can also use diesel. Like subways, their tracks are
fixed, making it difficult to adjust routes. Light-rail systems can be mixed with traffic in systems where cars
and buses share the road with the light-rail system. They also can have designated lanes and stops to allow pas-
sengers to get on and off the system easily. Light-rail systems are more expensive to build than bus systems,
but cheaper than subway systems. Their schedules are easier to adjust than those of a subway system but not as
flexible as a bus system.
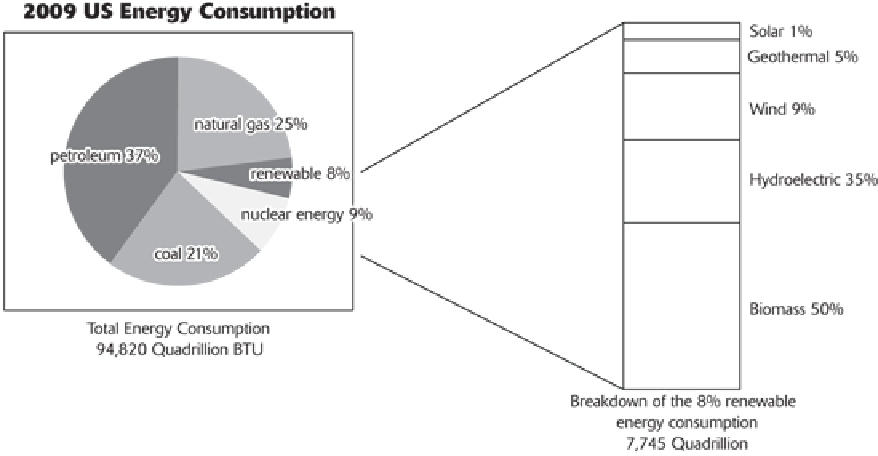
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy can be replenished without depleting supplies. There are several forms of renewable energy,
each with pros and cons. As shown below, approximately 6 percent of the total energy usage in the United
States is generated by renewable energy, which includes biomass, geothermal, hydroelectric, solar, and wind.
Other forms of renewable energy are being investigated.