Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Data Analysis
Distribution uniformity is often the primary measure of system performance, as
an irrigation system requires a high distribution uniformity in order to maintain
good crop yields, even though the water can be uniformly overapplied. Another per-
formance measure is application efficiency. Application efficiency is required with
relation to irrigation scheduling.
Solid set sprinkler
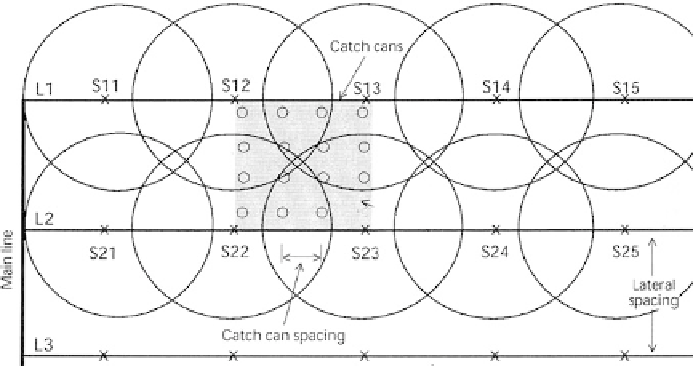
Determination of Distribution Uniformity (DU)
The DU is usually determined by measuring the depth of water falling into a grid
water depths in the catch cans. Sorting the catch can reading in ascending order, the
lowest quarter of values is determined. Then average the lowest quarter readings.
This average is then divided by the average of all the readings to give the distribution
uniformity as a percentage.
Fig. 4.2
Schematic of can setting for sprinkler evaluation
Application Efficiency
Application efficiency is calculated using the average depth of water applied, as
calculated above, and the volume of water applied. In order to convert the depth of
water applied to a volume, the depth must be multiplied by the irrigation target area.
Flow is measured as a nozzle discharge, and the average flow from the four nozzles
bounding the catch can grid is used as the measure of flow. The formula representing
application efficiency becomes
E
a
=
(catch can depth
×
grid area)
/
(average nozzle flow rate
×
irrigation duration)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search