Travel Reference
In-Depth Information
furnishing, and it is simply worth the time spent vis-
iting a Malay restaurant. Apart from that, the cus-
tomers also agree that convenient location motivates
them to patronize the restaurant.
For behavioural intention, the average mean
scores of the items are (M
negative consequences on customers' behavioural
intentions. This behavior may include negative
word-of-mouth, and intention not to revisit (Tax,
Brown & Chandrashekaren, 1996; Brown, 1997;
Liu, Furrer & Sudharshan, 2001; Susskind, 2002).
The results are similar to various studies (Zeith-
aml, et al., 1996; Alexandris, Dimitriadis & Mar-
kata, 2002) undertake in different settings thru out
the industries.
5.75, S.D, .124) with
items such as customers will attempt to influence
their friends and family to dine at a Malay restau-
rant with positive values. Satisfied customers said
that they will convince friends and family to dine at
Malay restaurant, dine out again at Malay restau-
rant, dine more often in Malay restaurant, recom-
mend Malay restaurants to someone else, and lastly
item indicates that the customers will consider
Malay restaurant as their first choice for next visit.
=
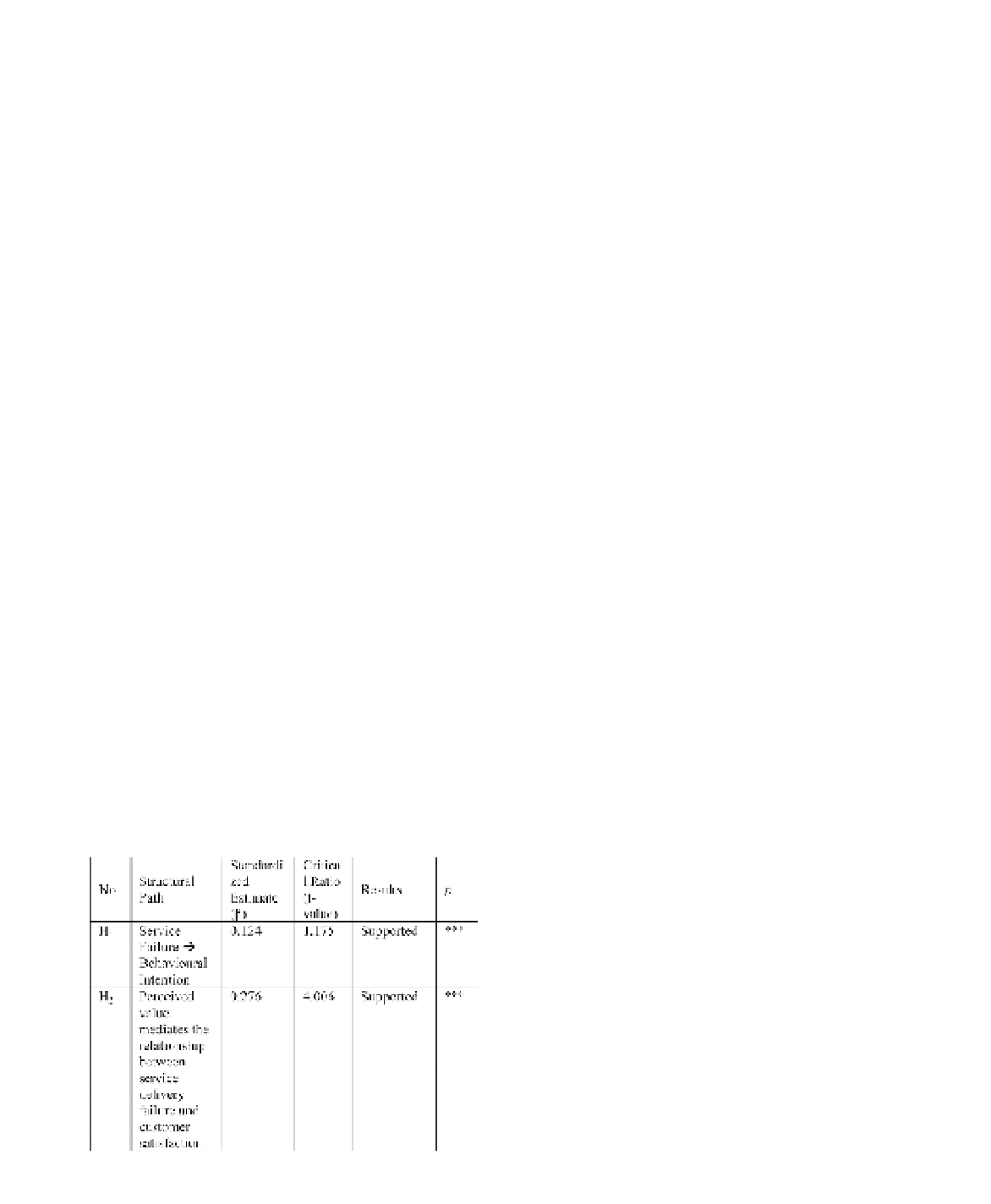
4.2.2
H2: Perceived value mediates the
relationship between service delivery failure
and customer satisfaction
The result of (
.001) showed
a significant relationship between the service fail-
ures and the customer satisfaction as mediated by
perceived value. Thus, essentially hypothesis H
6
is
supported. This finding is consistent with previous
studies that found there is a relationship between
service delivery failures and customer satisfaction
with perceived value as the mediating variables
(Cronin & Taylor, 1994; Dabholkar, Sheperd &
Thorpe, 2000; Akbar, Mat Som, Wadood & Alza-
idiyee, 2010). This proposition suggested that the
strength of the relationship between service deliv-
ery failures and customer satisfaction would be
increased or decreased by the presence of perceived
value. The test results reveal that perceived value
mediates the relationship between service delivery
failure and customer satisfaction.
β
:0.276, t:4.006, p
<
4.2
Hypotheses testing
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was adopted
in testing the paths which are hypothesized in
the model. Table 2 shows the result of the two
hypotheses.
4.2.1
H1: There is a significant relationship
between service failure and customer
behavioural Intention
The linkages between the service delivery failure
and behavioural intention received strong sup-
port in a significant relationship (
β
:0.124, t:1.175,
p
.001). This proposition is based on the belief
when failure occurred, customers that experience
that situation will eventually tend not to revisit the
premises which the scenario took place. The result
of this research showed a significant relationship
between the service delivery failures and behav-
ioural intention. This finding is consistent with
previous studies that found that when the posi-
tive service delivery failure happened there will be
<
5 DISCUSSION
Service delivery failures namely service fail-
ure, implicit or explicit customer requests and
unprompted and unsolicited employee actions are
found to be able to explain the variance in factor
affecting the service delivery failures happened in
Malay restaurant. It is found that factors such as
unpleasant smell, unbearable noise level, crowded
seating arrangement, insufficient seating arrange-
ment, failure to provide individual menu card,
and failure to comply to customer's specific food
request are among the items receiving critical atten-
tion from the customers as being the service fail-
ures typically encountered in Malay restaurants.
The other factor assumed contributing to posi-
tive customer satisfaction and behavioural inten-
tion is the roles of perceived value. This study
introduced perceived value as the new potential
variable to explain the service recovery-satisfac-
tion mismatch in Malay restaurant setting. Inter-
estingly, it demonstrated the presence of perceived
value able to shed some light on the otherwise
daunting and confusing service recovery-satisfac-
tion phenomenon. Perceived value is also found to
mediate the relationship between service delivery
Table 2. Correlation between service delivery system
failure and service recovery strategy.
Note
: ***Significant at p
<
.001.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search