Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
implicated in some of the major human
catastrophes of the past and present, and will
undoubtedly contribute to future suffering and
despair.
activities, particularly those involving
agriculture. Agricultural drought is defined in
terms of the retardation of crop growth or
development by reduced soil moisture levels.
This in turn may lead to economic definitions of
drought when, for example, dry conditions
reduce yield or cause crop failure, leading to a
reduction in income. It is also possible to define
drought in purely meteorological terms, where
moisture deficiency is measured against normal
or average conditions, which have been
established through long-term observations,
such as those illustrated in Figure 3.1 (Katz and
Glantz 1977).
DROUGHT
The problem of definition
Drought is a rather imprecise term with both
popular and technical usage. To some, it
indicates a long, dry spell, usually associated
with lack of precipitation, when crops shrivel
and reservoirs shrink. To others, it is a complex
combination of meteorological elements,
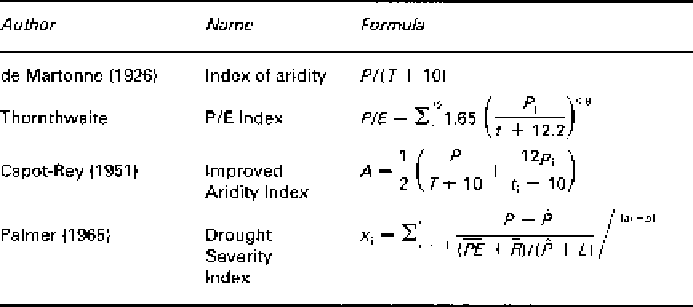
expressed in some form of moisture index (see
Table 3.2). There is no widely accepted
definition of drought. It is, however, very much
a human concept, and many current approaches
to the study of drought deal with moisture
deficiency in terms of its impact on human
Aridity and drought
The establishment of normal moisture levels also
allows a distinction to be made between aridity
and drought. Aridity is usually considered to be
Table 3.2
Examples of drought and aridity indices
Source:
After Landsberg (1986)
Symbols
P
mean annual precipitation (mm)
T
mean annual temperature (°C)
P
i
individual monthly precipitation (mm)
t
i
individual monthly temperature (°C)
^
climatically appropriate water balance for existing conditions
PE
annual potential evapotranspiration
L
loss (mm)
¯
mean monthly recharge
r
number of months