Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
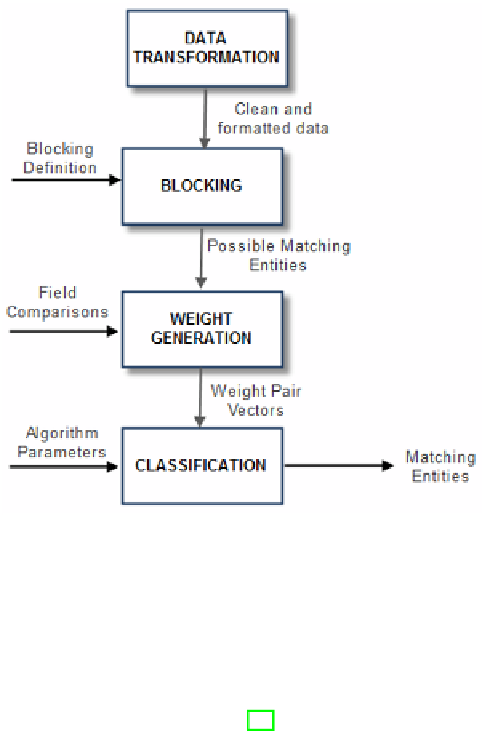
Fig. 5
The entity resolution process
standardised into a single common format. A fine grained division of data into sepa-
rate fields, such as storing the street, city and country in separate fields, is important
for high comparison accuracy. Approaches to automatically identify and standardise
this data based on hidden Markov models (HMM) and traditional dictionary based
lists have been studied by Churches et al. [24].
The data cleansing stage can have a direct effect on both the accuracy and speed
of the entire resolution process. Although some comparison functions on strings can
tolerate a threshold of dirty data, typically the more robust the function the more
expensive it is in terms of execution time [44]. The individual field comparison
method, is usually the most expensive aspect of any entity resolution process, there-
fore minimising the cost of these methods is desirable. The data cleansing stage can,
for example, convert shortened names such as “Mike” into “Michael” using lists be-
fore the field comparison stage. Although string comparison functions have come a
long way to identify similar stings, applying such data transformations in the data
cleansing stage can help to improve accuracy. It is important to note that most of
these transformations are domain dependent and specific to the type of data.
4.1.2
Blocking
If two data sets,
A
and
B
, are to be linked the complete number of comparisons
is equal to the cross product of the size of the two total datasets,
|
A
|×|
B
|
.When