Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Degree Distribution
Clustering Coef
# of Edges
true_ego: 34092
re: 1545
ff: 1230
# of Edges
true_ego: 34092
re: 1545
ff: 1230
1
5
20
50
500
5
10
50
500
degree
degree
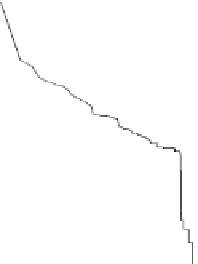
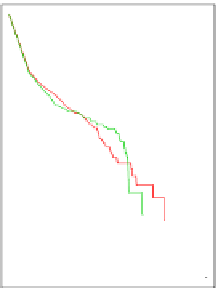
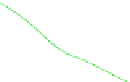
Fig. 4
Cumulative degree distribution and clustering coefficient estimation for one ego net-
work using a sample size of 5% of the total network. RE: Random Edge sampling. FF: Forest
Fire sampling
cumulative probability distributions,
D
are
the cumulative distribution functions. One of the limitations of the KS
D
statistic is
that it is more sensitive near the center of the distribution than at the tails. It might
be misleading to use this test to indicate whether two distributions are similar.
The Kullback-Leibler divergence (KLD), on the other hand, is a measure of dis-
similarity between two probability distributions in information theory. It is the ex-
pected log-likelihood ratio,
KLD
=
sup
x
|
F
(
i
)
−
G
(
i
)
|
,where
F
(
i
)
and
G
(
i
)
log
f
(
i
)
g
(
i
)
=
∑
i
f
(
i
)
where
f
(
i
)
represents the esti-
(
)
mated probability distribution and
g
represents the true probability distribution.
We use the KLD to have a measure for the whole body of the distribution so that im-
pact of mis-estimations at certain middle range degrees would not be as influential
as that in the KS statistic.
The final estimates presented in the following section are the averages across 20
replicates of the same experiments.
i
5.2
Results
Figures 5 displays the KS
D
statistics of the degree distribution estimations. The
eight plots present the eight ego networks. The number of nodes and the number
of edges of the true ego networks are labeled as ”V” and ”E” respectively in the
subtitles. Each line represents a different sampling method: solid lines represent
the RE, and dotted lines represent our method (labeled FF as it is based on the
Forest Fire algorithm). We can see that six out of eight the dotted lines are below
the solid lines when sample size (x-axis) is bigger enough (20-50%). Furthermore,
using the KS
D
measure, our method converges as the sample size approaches to