Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
NH
2
HN
O
NH
2
N
O
O
HN
NH
N
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
N
NH
HN
NH
2
O
N
O
O
N
HN
NH
2
NH
2
NH
2
c
H
2
N
H
2
N
O
O
HN
NH
NH
O
H
2
N
O
O
NH
NH
OH
H
2
N
HN
O
O
H
2
N
H
2
N
NH
2
Fig. 5
Dendrimers based gene vectors: (
a
) polyamidoamine dendrimers (PAMAM),
(
b
) poly(propylenimine) dendrimers, and (
c
) poly(L-lysine) dendrimers
PAMAM via a disulfide linkage, the transfection efficiency was significantly
increased.
In vivo
delivery studies were also performed to substantiate the useful-
ness of PAMAM for gene therapy (Tanaka et al.
2000
; Maruyama-Tabata et al.
2000
; Rudolph et al.
2000
). Whereas the good biocompatibility of PAMAM has
been well demonstrated by these studies, the
in vivo
transfection efficiency of
PAMAM is relatively low compared with the potent PEI25. Accordingly, efforts
have been made to chemically modify PAMAM to achieve better transfer
performances.
Uekama's group has systematically studied the effect of cyclodextrin modifica-
tion on the transfection capacity of PAMAM dendrimers (Arima et al.
2001
). All
the PAMAM derivatives conjugated with a-, b-, or g-CD showed potent luciferase
gene expression. The highest transfection was observed for a-CD conjugated


















































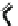





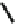






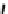
































Search WWH ::

Custom Search