Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
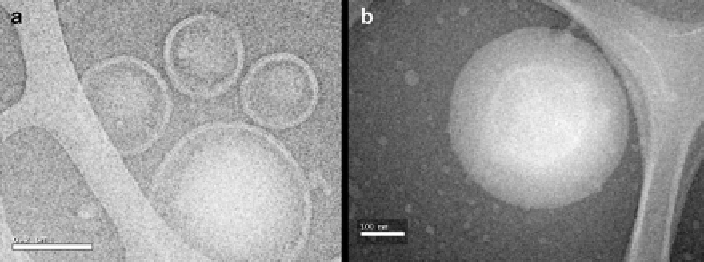
Fig. 11
(
a
) Cryo-TEM image of PEG-
b
-PMAazo444 vesicles at room temperature. Scale: 200 nm.
(
b
) Cryo-TEM image of PEG-
b
-PMAazo444 vesicles heated for 1 h at 90°C. Scale: 100 nm
3.2
Light Responsive Polymersomes
Stable, light-responsive polymersomes are attractive because the release of
entrapped species can be rapidly induced at specific time and location via exposure
to light. While pH, oxidation and reduction-responsive systems can also respond
quickly, they require that the chemical environment be modified by the addition of
acids or bases or other reagents. These environment changes may not necessarily
compatible with the drug targeting sites (in the case of applications in drug deliv-
ery) or with other applications such as controlled chemical reactions in microfluid-
ics. In contrast, light is a remote stimulus that does not require any chemical
environmental change and can be applied locally.
The first examples of light responsive polymersomes are built by incorporating
photo-responsive protein channels (such as Bacteriorhodopsin) in the membrane of
polymersomes (Choi and Montemagno
2005
). However, this case will not be fur-
ther discussed in this review because the responsiveness does not result from a
change of the membrane properties.
3.2.1
Systems with Photoactive Groups in Their Polymer Structures
The exposure of some photoactive groups to light can generate reversible structural
changes, thereby directly changing the hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance without
addition of other reagents. Typical groups that display photochemically-induced
transitions include azobenzenes (change of dipole moment, size and shape),
triphenylmethane leucohydroxide or triphenylmethane nitrile (generation of
charges), spyrobenzopyran (formation of zwitterionic species) and cinnamoyl
(photodimerization) (see Fig.
12
). These transitions can further induce changes in
the optical, mechanical and chemical properties of the system containing the chro-
mophore. Currently, these groups, especially azo derivatives, are intensively investigated
to implement light sensitivity in polymers (Pieroni et al.
1998
; Ikeda et al.
2007
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search