Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
in other species, prior opsonisation is often required to optimize uptake of liposomes
by Kupffer cells, highlighting a species difference in the mechanism of macrophage
targeting. Similarly, after subcutaneous injection of phosphatidylserine containing
liposomes into rats the retention of the lymphatically available dose in regional
lymph nodes is over 300% of the injected dose per gram, approximately three-fold
higher than subcutaneous administration of phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylg-
lycerol based liposomes (Oussoren and Storm
1997
).
By far the most common method of targeting drugs, DNA and cytotoxic agents
to the RES is by conjugation of sugars, particularly mannose (mannan, mannose
polymer) to the surface. These target the many mannose receptors present on the
surface of macrophages and monocytes. Although in general good targeting can be
achieved towards many organs of the RES via the use of sugars as targeting ligands,
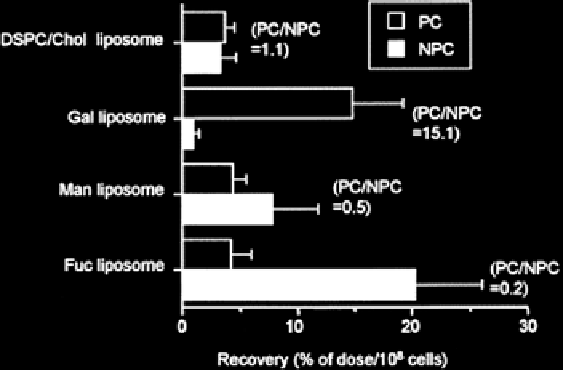
the cellular targets vary widely. This was demonstrated by Kawakami et al.
(Kawakami et al.
2000
) who prepared liposomes of approximately 90 nm in diam-
eter with 5% galactose-cholesterol, mannose-cholesterol or fructose-cholesterol.
Each of these liposomes rapidly distributed to the liver and spleen after IV dosing
to mice when compared to control liposomes without sugar, but distribution of
these liposomes into parenchymal (hepatocytes) versus non-parenchymal (Kupffer,
sinusoidal and stellate) cells was 15.1:1, 0.5:1 and 0.2:1 when compared to control
liposomes that were 1:1 (Fig.
9
). Hence, the choice of conjugated sugar can dictate
both the tissue biodistribution of the nanomedicine and the cellular disposition.
Others have reported over tenfold greater accumulation of galactose-conjugated
liposomes in hepatocytes than non-parenchymal cells, and seven to ten times
greater accumulation of mannose-conjugated liposomes in hepatocytes compared
Fig. 9
Hepatocellular localization of
3
H CHE from
DSPC/cholesterol liposomes
(85-95 nm
diameter) that were glycosylated, galactosylated, mannosylated or fucosylated 30 min after IV
administration in mice. Data represent mean ± s.d. (n = 3) in parenchymal cells (
PC
) and non paren-
chymal cells (
NPC
) in the liver (Reproduced from Kawakami et al. (
2000
). With permission)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search