Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Liver Biodistribution (30 h)
G4
Ph-disulphonate
60
40
G4
Ph-sulphonate
20
G3
Ph-sulphonate
G4
S
uccinat
e
0
Plasma size exclusion profiles
G4 S
u
ccinate
25000
G3 Ph-sulphonate
5000
20000
4000
15000
3000
10000
2000
5000
1000
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
10
2
0
3
0
4
0
50
G
4 Ph-su
l
phonate
G
P
h
-
s
u
p
h
n
a
4000
3000
3000
2000
2000
1000
1000
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
10
20
30
40
50
Elution time (min)
Elution time (min)
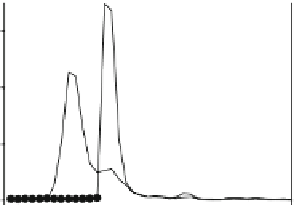
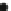
Fig. 7
Proportion of an IV dose of
3
H-labelled generation 3 (
G3
) and 4 (
G4
) polylysine dendrimers
conjugated with succinic acid (
succinate
), benzene sulphonate (
Ph-sulphonate
) or benzene disul-
phonate (
Ph-disulphonate
) identified in the liver of rats 30 h after dosing (5 mg/kg,
top panel
) and
size exclusion chromatography of each dendrimer diluted in phosphate buffered saline (
closed
symbols
) or preincubated in plasma at 37°C for 1 h (
open symbols
). The shift in the
3
H-peak to an
earlier elution time represents the formation of protein-bound dendrimer in plasma (Data taken
from Kaminskas et al. (
2007
))
3.5
Presentation of Ligands to Organs
of the Reticuloendothelial System
The previous discussion has focused mainly on particle properties that result in
intrinsic targeting towards macrophages of the RES. However, in some instances
macrophage targeting represents a therapeutic aim, rather than a negative conse-
quence of various particle properties. Examples include drug delivery to mac-
rophages involved in microbial or viral propagation (such as HIV infection), cancer





















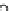




































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search