Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
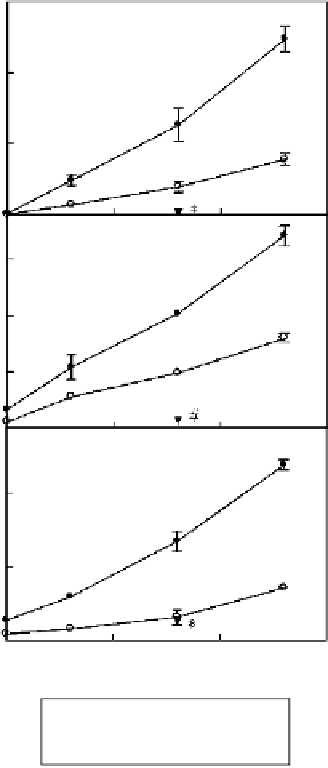
Figure 3.6 Quantification of CXC
chemokines released by astrocytes
stimulated with HMGB1.
The
experimental conditions were as
specified in the legend to
Figure 3.5;
*
p
0.05; #
p
0.01 versus cells
stimulated 24 hours with 40 nM
HMGB1.
Source: Ref.
[46]
. Copyright 2007.
The American Association of Immunol-
ogists, Inc.
30
20
10
0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
2
1
0
1
10 100
HMGB1 concentration (nM)
1000
8h HMGB1
24 h HMGB1
24 h HMGB1+PD098059
chemokines decreased markedly. Concerning the CXC chemokines transcriptionally
induced by HMGB1 (see
Figure 3.4
), we observed that CXCL1 and CXCL2 were
actively released by astrocytes stimulated with HMGB1 in a time- and concentration-
dependent manner (
Figure 3.6
).
Although astrocytes are probably the only source of chemokines containing the
ELR motif in the CNS, both neurons and astrocytes can respond to this chemokine
family because both express specific receptors for these chemokines
[67]
. The CXC
chemokine pathway has been associated with BBB compromise and the clinical
manifestation of autoimmune demyelination
[68]
. CXCL1 and CXCL2 seem to play
important roles in multiple sclerosis as chemoattractants of destructive immune cells
that form the characteristic infiltrates in areas of demyelination. Specifically, CXCL1,
a functional homologue of human IL-8, is mainly associated with neutrophil recruit-
ment from the blood, an early step of acute inflammation. Concurrence of CXCR2