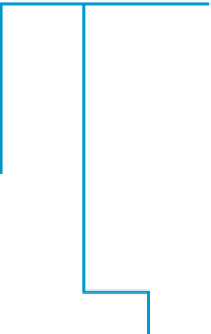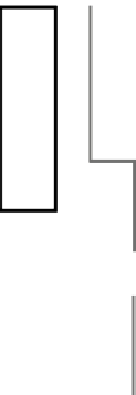Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
At this stage we may conclude that the entire host participates in APR to noxious
stimuli. These stimuli could be immunogenic, but need not be; they may be noxious
agents that cause tissue injury, but need not be: it is enough if the host simply senses
or anticipates danger. INIM mechanisms have a tremendous capacity to defend the
host from physical, chemical, and biological agents that may be harmful to the host.
The receptors involved sense antigen presence, inflammation, and injury (e.g., CTKs,
nerves), and also receive input from the CNS (e.g., conditioning). The
ADIM system
Infection, Injury
Homotopes, CTK, NPEP
INIM System
IL-1
β
, IL-6, TNF
α
, GMCSF,
INIR
Hypothalamus
CRH, VP
INIR
Innervation
INIR
Pituitary
APP
GC,
CAT
ACTH
GH,
PRL
Adrenal
Liver
APP
INIR
Fever
GC,
CAT
INIR
GC,
CAT
Tsr,
IL-7
Thymus
Apoptosis
Figure 1.2 Major regulatory circuits in NISS.
There are hierarchical regulatory circuits in the NISS, which are superimposed on each other.
For example, regulatory signals from a higher circuit (such as the CNS) dominate the signals
from lower circuits (e.g., pituitary). Pituitary hormones control the function of the adrenals,
gonads, thyroid, liver, and other tissues that secrete IGF. CTKs, which are tissue