Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
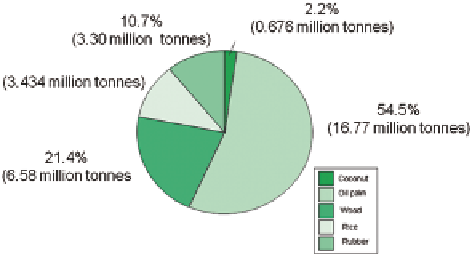
Fig. 11.1
Proportionate
annual production of agri-
cultural waste in Malaysia.
(Source: ESCAP
1997
)
11.2
Sources of Bio-compost
The materials inserted into compost heap possess a key effect on how sound the
composting mechanism works and the quality of the final product (compost). A
good composting must provide a diversity of materials and a reasonable C:N ratio.
Various kinds of microbes at work in the pile could provide very high probability of
achieving nutrient prosperous compost.
11.2.1
Agro-Industrial Wastes
Waste is an inevitable by-product of human actions. Better financial conditions and
life style in the Asian and Pacific region had increased the quantity and density of
generated waste. Agro-industrial waste disposal is a main problem in many indus-
tries around the world. The disposal of industrial wastes in the nearby areas causes
environmental dangers. The recycling of wastes is a disposal mechanism and re-
source management.
China harvests the biggest quantities of agriculture waste and crop residues fol-
lowed by India in the Asian and Pacific region. The quantities of waste that Malay-
sia produces from the palm oil, rubber, coconut, rice and forest products is illustrat-
ed in Fig.
11.1
(ESCAP
1997
). Nutrient requirement of crops by organic manures
as compost resulting from agro-industrial wastes is a major source of soil fertility
and crop productivity which reduces use of chemical fertilizers (Kayikcioglu
2013
).
11.2.1.1
Waste from Palm Oil Mill
Malaysia is the world's second biggest producer of palm oil in 2012, with a planted
area of 5.08 million ha, produced 18.79 Mt of crude palm oil (Malaysian Palm Oil
Board (MPOB)
2013
) with export potential of 18 Mt in 2011. Main importers of
Malaysian palm oil include China, India, USA and Pakistan.
Approximately 420 oil palm mills in Malaysia handle with the quantity of waste
created in the palm oil extraction process. About 5.5 t of fresh fruit bunch (FFB) are