Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
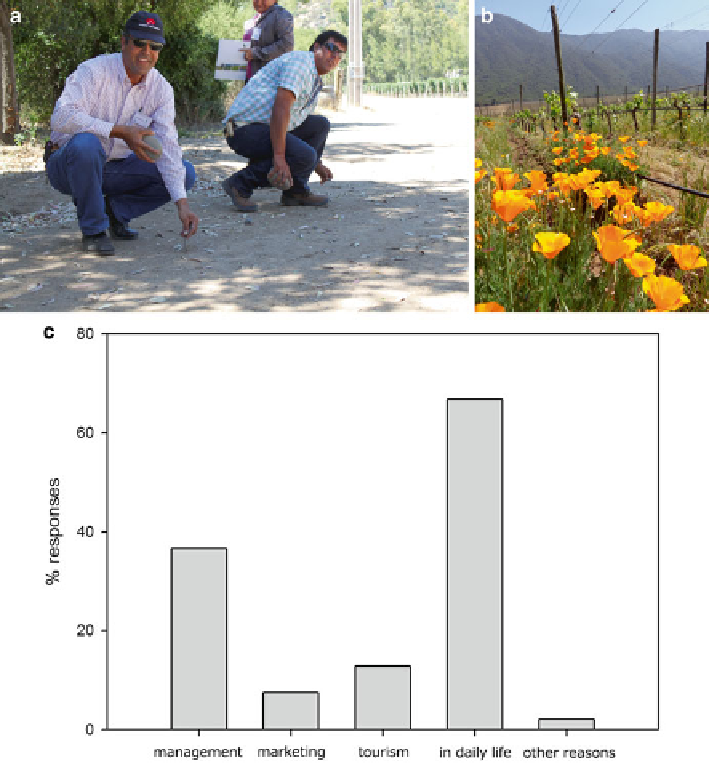
Fig. 19.3
(
a
) Workshop activities using the inquiry methodology (Feinsinger
1987
), evaluating
soil compaction between vineyards, road and native forest. (
b
) The use of
Eschscholzia californica
as a cover crop in farms that sustain high native species richness in surrounding areas, risking valu-
able ecosystems. Flower remains up to 4 years after initial seed plantation. (
c
) Interviews post
workshops showing responses on “in which areas they would like to apply what they learned
during this” (n = 98)
commercial options. One of the most popular mixes of cover crops includes
Eschscholzia californica,
even though it is a highly invasive species (Peña-Gómez
and Bustamante
2012
). The use of
E. californica
is common and has an ability to
grow everywhere. For this reason, it has been propagated by some wine producers
who have collected local seeds from roadways and trainlines because they believed
erroneously that this would contribute to preserving local genetic diversity
(Fig.
19.3b
). Therefore they were applying correct restoration techniques but with
Search WWH ::

Custom Search