Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
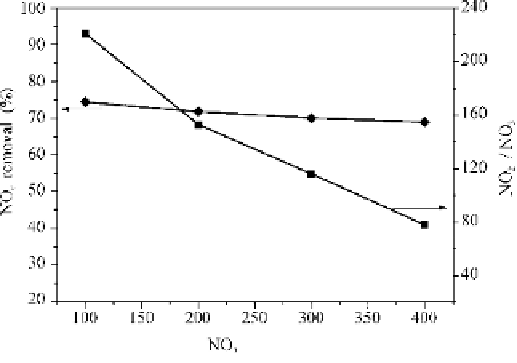
initial NO
2
concentration, accompanied by a small drop in the NO
2
removal
efficiency.
Fig. 4.10
NO
2
removal efficiency at different initial concentrations with the existence of S(IV)
(ppm)
4.5 Simultaneous Removal of SO
2
and NO
2
Obviously, the SO
2
absorption in the liquid phase mostly leads to an increase in
the tetravalent-S concentration and a decrease in the pH value. Meanwhile, the
NO
2
absorption behavior lowers both the pH value and tetravalent-S concentration.
The interactions between SO
2
and NO
2
must be clearly understood so as to
increase the simultaneous removal efficiencies of multi-pollutants.
4.5.1 Effect of SO
2
on NO
2
Removal
In the related experiments, the pH value and tetravalent-S concentration was kept
at 5.5 and 0.01 mol/L, respectively, while the SO
2
concentration was adjusted
within 0 - 500 ppm to form a series of test settings. As shown in Fig. 4.11, results
suggest that the SO
2
effect on the NO
2
removal efficiency is negligible. That is,
the removal efficiency slightly decreases from 70% to 67% as the SO
2
concentration increases in 0 - 500 ppm. This observation occurs because of the
dual roles of the SO
2
absorption: (i) promoting the reactions listed in Eqs. (4.10)
and (4.11) by increasing the tetravalent-S concentration; (ii) decreasing the pH
Search WWH ::

Custom Search