Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
collection and storage stages of the absorption solution before ion chromatography
measurements.
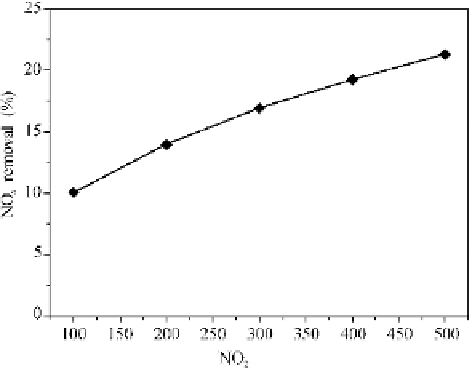
Fig. 4.5 shows the effects of the initial NO
2
concentrations on the removal
efficiency by using water. The removal efficiency increases with the initial NO
2
concentration. This occurs because that with increasing the NO
2
concentration in
the gas phase, the concentration gradient between gas and liquid increases and the
partial pressure of NO
2
at the interface becomes larger. Consequently, the NO
2
solubility coefficient in liquid membrane increases, leading to an increased pattern
appearing respectively in the reaction rate in Eq. (4.3) and in the NO
2
absorption
rate. Finally, the NO
2
removal efficiency increases.
(ppm)
Fig. 4.5
Effects of the initial concentration of NO
x
on the removal efficiency by water
4.4 Effect of Tetravalent-S Components on NO
2
Removal
It is thought that the existence of reductive substances in the WFGD solution, such
as SO
3
2
and HSO
3
of the solubilized SO
2
in the absorption liquid, can impel NO
2
to react with themselves, thereby increasing inevitably the removal efficiency by
improving the enhancement factor in the chemical reaction absorption and
advancing the mass transfer rate. In this subsection, the attention was initially
focused on the Na
2
SO
3
effect on the NO
2
removal in the solution, so as to validate
the NO
2
removal improvement of reductive substances. Afterward, combined with
the added Na
2
SO
3
, the pH effect was considered.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search