Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
After screening, transgenic plants are established by conventional
techniques and represent the T
0
generation. A preferred technique is to
establish plantlets by in vitro grafting of regenerated sunflower shoots from
split embryonic axis explants. T
0
plants are used as pollen donors to obtain
T
1
and T
2
as successive hybrids with sunflower elite lines. The primary
transformants are typically small and stunted but T
1
plants are normal.
Transgenes are usually dominant in their inheritance and segregate in a
regular Mendelian fashion, but several copies of T-DNA are the rule (2 to
10), sometimes as incomplete, truncate segments.
9.3.3 Intended Transgenic Sunflower Releases
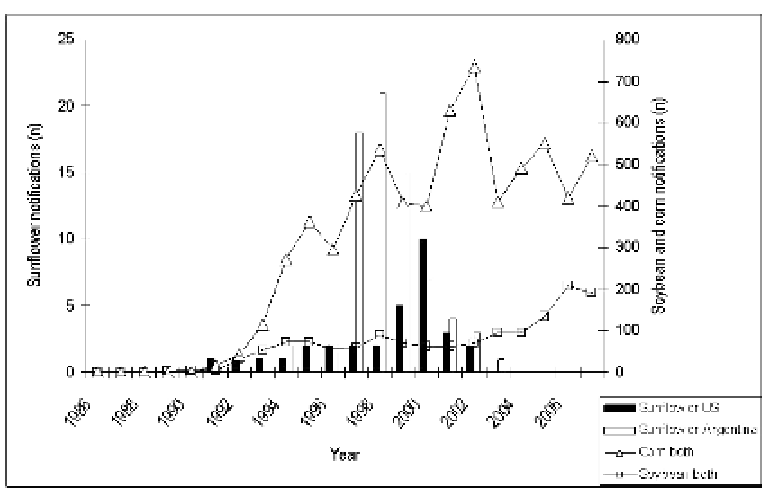
Since 1991, there was a continuous growth in a number of environmentally-
However, since 2000 sunflower notifications have declined , both in the US
and in Argentina, compared to corn and soybean notifications. Private seed
companies have concentrated their efforts in three agronomically important
transgenic traits: the oxalate-oxidase expressing gene for fungal disease
control, glyphosate tolerance by expressing
Agrobacterium
EPSPS gene
cp4
,
Oxalic acid is a key component of infection by
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
and other fungi. The enzyme oxalate oxidase confers disease resistance
through the activation of defense genes in transgenic sunflower plants
Figure 9-3
Number of GM sunflower environmental release (bars), GM corn and GM
soybean in the US and Argentina. Sources:
http: //www.isb.vt.edu/cfdocs/isblists2.cfm?opt=4
Search WWH ::

Custom Search