Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 103
Posterior respiratory cone of a shore fly
larva - family Ephydridae.
Fig. 105
Wing venation of an agromyzid fly - family
Agromyzidae (genus
Cerodontha).
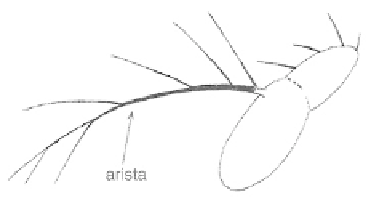
Fig. 104
Antenna of a small fruit fly - family
Drosophilidae (genus
Scaptomyza).
borne on a pair of pointed, posteriorly directed
cones
(Fig. 103).
EXAMPLES:
Notiphilinae -
Hydrellia griseola
(larva
= a cereal leaf miner); Ephydrinae -
Scatella
spp. (glasshouse wing-spot flies).
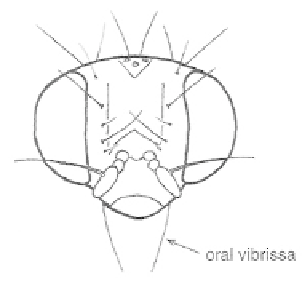
Fig. 106
Head of an agromyzid fly - family
Agromyzidae.
19. Family DROSOPHILIDAE
(small fruit flies)
(p. 185
et seq.)
21. Family AGROMYZIDAE
(p. 186
et seq.)
A large family of small, mainly black or grey,
often yellow-marked flies with a distinct break
on the costal vein
(Fig. 105);
oral vibrissae
present
(Fig. 106).
Larvae with main axis of
the mouth-hooks set obliquely or at right angles
to the rest of the mouthparts and each usu-
ally with two or more equally sized teeth
(Fig.
107);
dorsal elements (dorsal cornu) of the
cephalopharyngeal skeleton (mouthparts) undi-
vided (= subfamily Phytomyzinae)
(Fig. 107a)
or
divided into two (= subfamily Agromyzinae);
anterior spiracles arising dorsally and relatively
closely set; posterior spiracles prominent. The
larvae usually mine within leaves or stems, often
forming distinctive galleries in which two discon-
tinuous trails of frass are visible.
EXAMPLES:
Agromyzinae -
Agromyza poten-
tillae (larva =
strawberry leaf miner),
Very small to small flies with bright red com-
pound eyes; arista of antenna usually plumose
and with a bifid tip
(Fig. 104);
anal cell present.
Larvae maggot-like, with elongated anterior and
posterior respiratory processes and anal tuber-
cles; anterior spiracles sometimes absent.
EXAMPLES:
Drosophila
spp. (small fruit flies),
Scaptomyza flava.
20. Family BRAULIDAE
Minute, apterous, superficially hippoboscid-like
flies, adapted for life as ectoparasites of bees.
Larvae plump, with distinctive anterior and pos-
terior sensorial processes. The larvae inhabit bee
colonies and feed on wax and stored pollen.
EXAMPLE:
Br aula coeca
(bee-louse).