Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
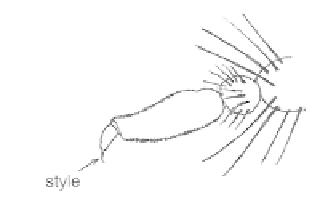
Fig. 91 Antenna of a horse fly - family Tabanidae.
Fig. 90 Larva of a gall midge - family
Cecidomyiidae: (a) sternal spatula.
inconspicuous. Most species are phytophagous,
many inhabiting plant galls, but some
are predacious on mites and other small
invertebrates.
EXAMPLES:
Contarinia pisi
(pea midge),
Dasineura brassicae
(brassica pod midge),
Haplodiplosis marginata
(saddle gall midge),
Mayetiola destructor
(hessian fly),
Resseliella
theobaldi
(raspberry cane midge),
Sitodiplosis
mosellana
(orange wheat blossom midge).
Fig. 92 Antenna of a therevid fly - family
Therevidae.
91); mouthparts of females adapted for piercing
and capable of inflicting a painful 'bite'. Larvae
occur in damp situations, where they are carnivo-
rous on soil-dwelling invertebrates.
EXAMPLES:
Chrysops
spp. (deer flies),
Haematopota crassicornis
and
H. pluvialis
(common clegs),
Tabanus
spp. (horse flies).
Suborder BRACHYCERA
Usually stout-bodied flies with short, 3-
segmented antennae which often terminate in a
distinct apical style; palps 1- or 2-segmented and
porrect. Larval head incomplete, generally re-
tractile, and with vertically biting mandibles.
Pupae usually obtect, the adult emerging
through a straight or a T-shaped slit.
This suborder includes clegs, horse flies
(family Tabanidae) and various predatory
groups (e.g. families Asilidae, Dolichopodidae,
Empididae and Therevidae) but no species that
cause significant harm to crops.
9. Family THEREVIDAE (stiletto flies)
Distinctly pubescent, thin-legged flies; antennae
with a small style
(Fig.
92); abdomen slender
and pointed posteriorly; non-predatory. Larvae
white, elongate and snake-like, with obvious
segmentation; predacious on various soil
invertebrates.
EXAMPLE:
Thereva nobilitata
(common stiletto
fly).
8. Family TABANIDAE
(clegs, horse flies, etc.)
10. Family HYBOTIDAE (dance flies)
Medium-sized to large, robust, blood-sucking
flies with very large compound eyes; squamae
large; feet with three arolia; antennae without a
style but with the third segment annulated (Fig.
Members of this family (formally included as a
subfamily within the Empididae) are important
predators of agricultural pests. The adults feed