Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
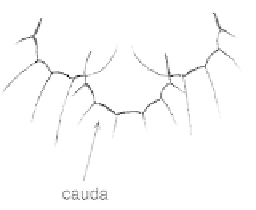
Fig.
38 Cauda and bilobed subanal plate - family
Drepanosiphidae.
Fig.
40 Venation of an alate aphid - subfamily
Pemphiginae.
Myzus persicae
(peach/potato aphid),
2
Rhopa-
losiphum padi
(bird-cherry aphid),
Sitobion
avenae
(grain aphid).
20. Family PEMPHIGIDAE
(p. 121
et seq.)
Aphids with the terminal process of the anten-
nae short
(Fig. 37c);
antennae of winged forms
often (e.g. subfamily Pemphiginae) with annu-
lated segments
(Fig.
40); compound eyes re-
duced to three facets; siphunculi stumpy cones,
pore-like or absent; cauda broadly rounded;
body often with groups of well-developed wax
glands; venation varies according to subfamily
but Rs vein of forewing present and origins of
Fig.
39 Venation of an alate aphid - family
Aphididae.
faceted; siphunculi varying from short to very
long cylinders, sometimes noticeably tapered or
swollen and often flanged apically; cauda
broadly tongue-shaped to finger-shaped; Rs vein
of forewing present, forewings and hindwings
with Cu
t
and Cu
2
and origins of these veins well
separated
(Fig.
39). Many species show an alter-
nation of generations, having a primary (winter)
host upon which asexual and sexual reproduc-
tion occurs and eggs are laid, and a secondary
(summer) host upon which development is en-
tirely asexual, parthenogenetic and viviparous.
Migration between these alternate hosts is usu-
ally achieved following the production of winged
forms. Aphids are commonly known as 'black-
flies' or 'greenflies'.
EXAMPLES:
Aphis fabae
(black bean aphid),
Brevicoryne
2
For many years, common names of certain
heteroecious species of aphid (i.e. those with different
winter and summer host plants) have included refer-
ence to both kinds of host, separated by a hyphen, that
of the primary (winter) host having priority (e.g.
willow-carrot aphid). This introduces potential confu-
sion with common names hyphenated for other rea-
sons (e.g. bird-cherry aphid). In recognition of this
problem, some authors have used either an 'em' or an
'en' dash between the alternate host names but this
subtlety is not always followed, probably being largely
overlooked or misunderstood. In view of these diffi-
culties, and to avoid ambiguity, a solidus (forward
slash) is used in the present work to delineate primary
and secondary hosts in such common names.
brassicae
(cabbage
aphid),