Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
4.14
Calmodulin-Binding Proteins
4.14.1
Function of Calmodulin-Binding Proteins
in Different Signaling Systems
Calmodulin (CaM) is a small (~150 residues), acidic protein comprised of a fl exi-
ble central helical region which joins two globular domains, each with two Ca
2+
-
binding EF-hand motifs (Gilford et al.
2007
). Upon binding to Ca
2+
, the hydrophobic
surfaces in each globular domain are exposed which then interact with the charac-
teristic amphiphilic structure, called calmodulin-binding domain (CBD), present in
calmodulin-binding proteins (CBPs) (Reddy
2001
; Snedden and Fromm
2001
;
Reddy et al.
2002a
,
b
). This interaction leads to conformational changes in CBPs
and modulation of their activity. The specifi city of a response evoked due to
characteristic Ca
2+
signature may depend upon the expression kinetics of CBPs
(Ali et al.
2003
).
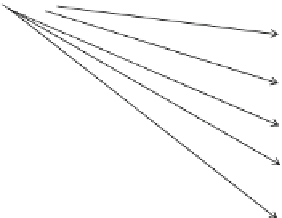
CaM binds to a variety of proteins involved in various signaling systems
(Fig.
4.5
). These include proteins involved in pathogen-associated molecular pattern
(PAMP) - receptor mediated signaling pathway (receptor-like kinases), Ca
2+
signal-
ing system (CNG ion channels; Ca
2+
-ATPases, Ca
2+
-CaM-dependent kinases), reactive
oxygen species (ROS) signaling system (NAD kinase,
BAG
gene), redox signaling
Receptor-like kinases
CNG channels
Ca
2+
-ATPases
Ca
2+
-CaM-dependent kinases
NAD kinase
Catalase
CAM-
binding
proteins
NO synthase
MAPK phosphatases
Calmodulin binding
transcription factors
(CAMTAs)
WRKY transcription factors
MYB transcription factors
TGA transcription factors
Homeodomain transcription
factors
Fig. 4.5
Calmodulin-binding proteins





Search WWH ::

Custom Search