Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
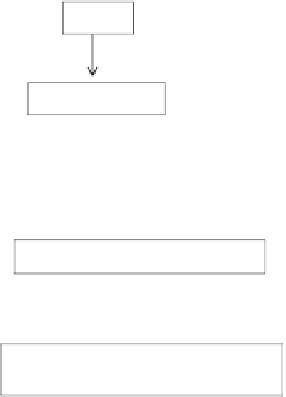
PAMP
Activation
Anion channels
Anion efflux
Plasma membrane depolarization
Activation of membrane depolarization-
activated Ca
2+
-permeable channels
Increased Ca
2+
influx
Increase in
cytoplasmic Ca
2+
Activation of S-type anion channels
Fig. 4.3
Role of anion channels in induction of Ca
2+
infl ux by PAMPs
4.8
K
+
Channels in Ca
2+
Infl ux
The major function of K
+
channels is in regulation of membrane voltage control
(Maathuis et al.
1997
). The K
+
channels play a role in regulating both the infl ux and
effl ux of K
+
from cells (Maathuis et al.
1997
). Two types of K
+
channels have been
identifi ed, each with a characteristic voltage dependence, one opens in hyperpolar-
izing (inward rectifying K
+
channel, K
+
in
) and another opens at depolarizing
(outward- rectifying K
+
channel, K
+
out
) conditions. Stimulation of H
+
-ATPase will
hyperpolarize the membrane and direct the K
+
gradient inward, while anion channel
activation will depolarize the membrane and enhance the activity of K
+
out
channel
activity (Maathuis et al.
1997
).
Membrane depolarization (White
2000
) or hyperpolarization (Pei et al.
2000
)
triggers Ca
2+
channel activation as part of the Ca
2+
signaling system. K
+
channels
regulate both depolarization and hyperpolarization of cell membrane (Maathuis


Search WWH ::

Custom Search