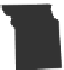Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
site grading. These land surveying systems have much in common with
the geographic coordinate system in that they all are based on a base
reference. In the United States the base referencing system includes a
base line and principal meridian (equivalent to a longitude line) called a
meridian (similar to latitude lines running parallel to the equator). The
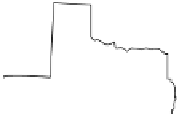
next level of grid subdivision established by the U.S. federal government
utilizes a grid of township and range lines called the Public Land Survey
System (see Figures 6.7 and 6.8). The U.S. Geological Survey and the U.S.
Bureau of Land Management manage this system. With each acquisition
of land territory (California-Arizona, Washington-Oregon, or Alaska) a
base reference or meridian was surveyed with physical markers (sur-
veying monuments) placed in the ground as permanent markers, in
the form of a brass disk mounted on concrete or hard stone, or in some
cases placed on what are called witness trees (see Figure 6.9-A, a USGS
survey monument, and 6.9-B for a Chinese example). The markers and
their location were entered in a national registry, making them traceable
for future surveying activities such as establishing property lines, road
and railway rights-of-way, and municipal and county boundaries.
Principal Meridians
and
Base Lines
Governing
The United States
Public Land Surveys
Figure 6.7
Township and range: the Public Lands Survey System