Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 1
Part-worth utilities
for EF
in line with prospect theory we find that positive variations of equal amount are
valued less than negative variations and, in our case, this is testified by both inner
variations [Beta
EF3-2
(0.637) \ Beta
EF3-4
(1.062)] as well as by outer variations
[Beta
EF1-2
(0.176) \ Beta
EF4-5
(0.828)]. Similar considerations also apply to
PLUBF (see Fig.
2
).
In order to analyze the impact of different estimation methods, define and
measure the potential biases for policy implementation one can use WTP/WTA to
avoid scale problems that would, otherwise, fraud the comparison.
As it is well documented in the literature (Daly et al.
2010
) there are different
methods that can be used to test the statistical significance of the ratio of coeffi-
cients between the desired attribute and the monetary one representing the base of
any WTP/WTA measures.
Testing the statistical significance of the ratios is not only important per se,
since it allows the researcher to infer reliability of the results obtained especially
when using them for simulation purposes, but also because it is reasonable to
assume some heterogeneity in the sample selected. Especially in connection with
this last point and for policy evaluation purposes it is interesting to estimate
monetary confidence intervals rather than using single point estimates.
Among the methods that one can use to construct confidence intervals for these
ratios the most popular are: (1) Krinsky and Robb (Krinsky and Robb
1986
,
1990
);
(2) Bootstrap (Efron
1979
; Mooney and Duval
1993
; Efron and Tibshirani
1993
);
(3) Delta Method (see e.g. Greene
2003
). In our case we opted for this last method.
WTP are assumed normally distributed and, thus, symmetrical around the mean.
Delta Method's estimates of the variance of a non-linear function of two random
variables is obtained by taking a first-order Taylor expansion around the mean
value of the variables and calculating the variance for this expression (Hole
2007
).
Our choice is motivated by two main considerations: (1) Delta Method is an
exact method compared to both Krinsky-Robb and Bootstrap where a simulated
distribution for the variable of interest is generated; (2) Shanmugalingham (
1982
)
has empirically shown that the normality assumption underlying the Delta Method
is, in general, less tenable when the standard deviation of the denominator variable












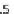


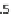




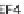



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search