Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
N
OH
CF
3
N
HO
HN
N
OH
O
Cl
O
HO
CF
3
Fluridone
Norflurazon
NDGA
F
F
O
R
N
N
HO
OCH
3
H
3
CO
H
3
CO
Compound 13; R=SC
2
H
5
Compound 17; R=SC
6
H
5
OCH
3
O
OCH
3
OCH
3
O
AbamineSG
Abamine
SLCCD inhibitor
(b)
N
N
O
N
Cl
Cl
O
OH
OH
OH
Cl
O
N
NN
N
NN
N
NN
Uniconazole
Abscinazole-E2B
Diniconazole
OH
OH
OH
COOH
COOH
COOH
O
O
O
(+)-8 -methylidyne-ABA
(+)-9 -acetylene-ABA
(+)-9 -vinyl-ABA
O
H
OH
COOH
AHI4
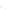
Fig. 2.4
Inhibitors of ABA biosynthetic and catabolic pathways.
a
ABA biosynthetic inhibitors.
These chemicals inhibit phytoene desaturase or NCED activity. Abbreviation:
NDGA
nordihy-
droguaiaretic acid.
b
ABA catabolic inhibitors. Both the azole types (uniconazole, diniconazole,
and abscinazole-E2B) and ABA analogues shown in this figure inhibit CYP707A activity
Nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) is an inhibitor of lipoxygenase, which
catalyzes dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (Fig.
2.4
). NDGA is sup-
posed to inhibit carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases including NCED (Creelman
et al.
1992
). The application of NDGA to osmotically stressed soybean suspension
cells inhibited the accumulation of ABA (Creelman et al.
1992
). Abamine was first
developed as an NCED-specific inhibitor based on the structure of NDGA (Han
et al.
2004
). Abamine inhibited ABA production in osmotically stressed spinach
leaf disks more effectively than NDGA (Han et al.
2004
). Kitahata et al. (
2006
)
further improved abamine to generate abamineSG, which has increased specific-
ity for NCED without the growth retardation effect seen in abamine. Abamine
and abamineSG inhibited ABA accumulation by 35 and 77 %, respectively, and
acted as inhibitors of cowpea NCED in vitro with
K
i
values of 38.8 and 18.5
ʼ
M,







































































































































































































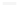



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search