Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
developmental, and metabolic process following a rhythmic pattern within a period of
24 h, in clear coordination with the diurnal cycle (Hubbard et al.
2009
; de Montaigu
et al.
2010
). These diurnal oscillations are known as circadian rhythms and the endog-
enous mechanism responsible for generating and maintaining this rhythmicity is
called circadian clock (Wijnen and Young
2006
). Until the present day the circadian
clock has been found to be present in almost all organisms studied from photosyn-
thetic bacteria to higher plants and mammals (Harmer
2009
; Más
2008
; McClung
2008
). Some examples of circadian rhythms include the sleep-wake cycles in ani-
mals, locomotor activity in insects, or photosynthesis and leaf movement in plants.
The presence of circadian rhythms has been suggested to be advantageous to adapta-
tion (Dodd et al.
2005
; Ouyang et al.
1998
; Woelfle et al.
2004
), allowing the organ-
isms to coordinate their physiology and metabolism anticipating the environmental
changes result of the day/night transitions. Furthermore, the circadian clock allows
to temporally separate biological, physiological, or metabolic incompatible process
such as feeding and sleeping, nitrogen fixation and photosynthesis or anabolism and
catabolism (Golden et al.
1997
; Vollmers et al.
2009
; Yang
2010
).
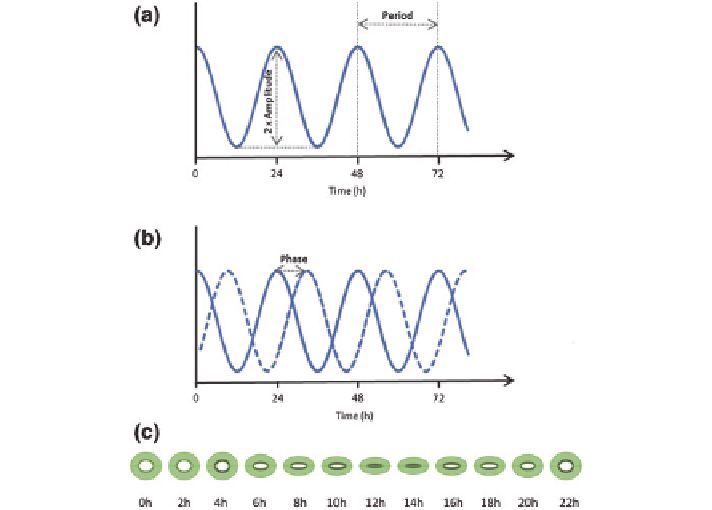
Circadian rhythms exhibit a 24-h cycle that can be represented as a sinusoi-
dal function, defined by certain parameters such as amplitude, phase, and period
(Fig.
19.1
). This oscillation is sustained even in the absence of environmental
Fig. 19.1
Schematic representation of the mathematical parameters used to define the circadian
oscillation.
a
The period is defined as the time between a specific phase of the cycle and when
this is repeated again. The amplitude is defined as the difference between the maximum (or mini-
mum) and the average value of the rhythmic parameter studied.
b
The phase is defined as the
state of an oscillation relative to another reference rhythmic oscillation.
c
Schematic representa-
tion of the circadian oscillation of stomatal aperture
Search WWH ::

Custom Search