Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
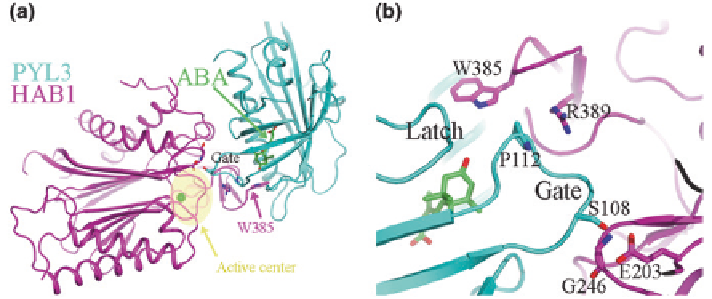
Fig. 7.6
PYL3-ABA-HAB1 complex structure.
a
Overall structure of PYL3-ABA-HAB1
complex (pdb ID: 4DSC). Active center of PP2Cs is shown in
pale yellow
.
b
The interface
between PYL3 and HAB1 in the PYL3-ABA-HAB1 complex. S108 of PYL3 contacts with
G246 and E203 of HAB1. P112 of PYL3 stacks with R389 of HAB1. W385 of HAB1 inserts the
binding pocket. ABA,
green
; PYL3,
cyan
; HAB1,
magenta
affinity between PYLs and ABA. And finally, the activity of PP2Cs is inhibited by
binding to PYLs.
As mentioned above, PYR1, PYL1, PYL2, and PYL3 are homodimers in their
apo states, but the binding ratio between PYLs and PP2Cs is 1:1 in the PYLs-
PP2Cs complex structure. Even interestingly, the homodimer interface encom-
passes the region that plays an important role in interacting with PP2Cs. So, how
can the dimeric PYLs bind to the PP2Cs? From the analysis of the structures of
dimeric PYR1, PYL1, PYL2, PYL3, the dimeric interfaces mainly appeared on
the gate loop and the C-terminal
ʱ
-helix (see Fig.
7.7
a, b), showing that fixation
of the gate loop in the dimeric interface prevents the binding of PP2Cs to the gate
loop. Therefore, before the receptor binds to the downstream proteins (PP2Cs),
the dimeric PYLs need to be dissociated. Receptor dimerization may therefore be
a mechanism to reduce basal receptors-downstream proteins interaction (PYLs-
PP2Cs), by blocking downstream activity. Significantly, the binding of ABA
to dimeric PYLs does not disrupt the dimerization. Once ABA binds to dimeric
PYLs, the gate loop of PYLs changes its conformation to close the gate, and the
relative distance between these two PYLs protomers becomes larger. These two
changes rearrange the interface residues, bring about the decrease of van der
Waals contact and hydrogen bonds at the dimeric interface (see Figs.
7.3
b and
7.7
b). Hence, the binding of ABA induces the closure of the gate loop, generates
a platform to interact with PP2Cs, further weakens the dimerization interaction,
and finally facilitates the dissociation of dimeric PYLs to form a 1:1 PYLs-PP2Cs
complex.
In the above-mentioned ABA signaling pathway, ABA first binds to PYLs, and
then the PYLs-ABA complex binds to the downstream PP2Cs; this process is
called the induced pathway. However, some PYLs do not need ABA to inhibit the
phosphatase activity of PP2Cs; this process is called the constitutive pathway.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search