Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Complementarity
(
Natural System, N
)
(
Formal System, F
)
2
Energy
Information
6
1
8
5
4
3
Matter
Knowledge
7
(
Body
)
(
Mind
)
Complementarity
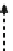
Fig. 21.1
The suggested qualitative (or
complementary
) and quantitative (or
supplementary)
relations among
energy
,
matter
,
information
, and
knowledge
. The meanings of the numbered
arrows are explained in Table
21.2
.
Mattergy
- the combination of matter and energy that is
conserved in the Universe, according to the First Law of thermodynamics.
Infoknowledge
- a new
term coined by combining
information
and
knowledge
in analogy to mattergy. Unlike mattergy
which is conserved,
infoknowledge
may increase with time
Table 21.2
The integration of the ideas of Rosen (1991), Burgin (2004), Polanyi (1958/62), and
Stenmark (2001) within the framework of the postulated “mattergy-infoknowledge complemen-
tarity” depicted in Fig.
21.1
. The various symbols appearing in this table are E = energy; m = mass;
c = speed of light; H = Shannon entropy;
p
(x) = the probability of the occurrence of event x; S =
thermodynamic entropy; k = Boltzmann constant; W = the variety of molecular configurations
compatible with thermodynamic constraints; C = channel capacity of a communication system;
B = bandwidth of the communication channel; P = power of the message source; N = noise of the
communication channel
Arrows and
nodes in
Fig.
21.1
Authors
Meaning or referent
M. Burgin
(2004,
2011a)
1
“Contains”
4
“Contains”
2, 6
“Similar”
3, 7
“Similar”
1, 2, 3
and 4
The “fundamental unit of knowledge,” with the following
identification of the
nodes
in Scheme 3 in Burgin (2004,
2011a) and those in Fig.
21.1
Matter
“U” or objects of knowledge
Energy
“W” or intrinsic properties of objects
(continued)