Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
dynamic system whose structure and function are driven by a system of such
coincident events, and we can identify such a system with an organism, unicellular
or multicellular. Viewed in this manner, cells and their higher-order systems whose
structure and properties ultimately depend on enzymes can be naturally associated
with a 4-dimensional space. In other words, living systems are 4-dimensional
and can be projected onto either the traditional 3-dimensional space of Euclid at a
given time (span) or the one-dimensional space of time under a given spatial
arrangement.
15.11 Allometry
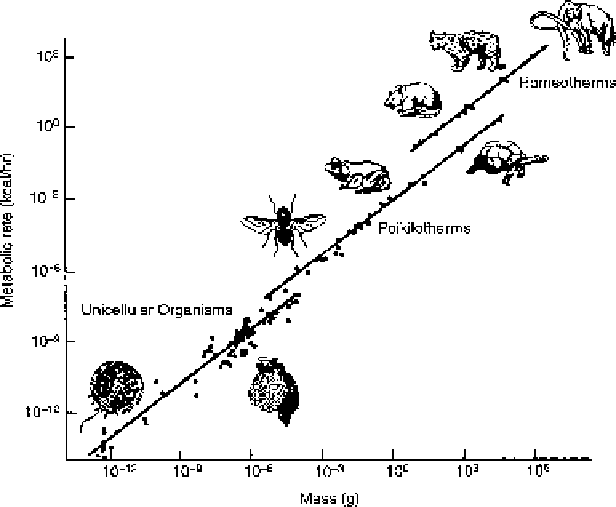
Allometry is the study of the effect of the size of an organism, either unicellular or
multicellular, on its function. For example, the linear relation between metabolic
rates and body mass of different organisms shown in Fig.
15.13
is the subject of
intense studies in the field of allometry. Whitfield defines
allometry
as follows
(2006, p. 58):
Fig. 15.13 The relationship between the metabolic rate of various organisms and their body mass
(Reproduced from Whitfield 2006, p. 77 with kind permission from Novo Nordisk, Inc.)