Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 12.14 Five mechanisms of transmembrane signaling in cells. The table was reproduced
from Fig.
2.8
, p. 18 in Katzung (2001)
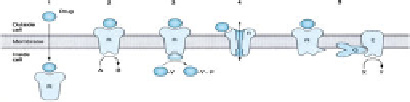
Transmembrane signaling mechanisms
Mechanism Ligand (first messenger)
Receptor
Second messenger
1
NO
Guanyl cyclase
cGMP
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoid
receptor/hsp90
Glucocorticoid receptor
2
Insulin, EGF, PDGF, ANF,
TGF-
b
, etc.
Receptor tyrosine kinase Phosphorylated target
proteins
Receptor serine kinase
Receptro guanyl cyclase
3
Cytokines (interferons,
interleukins, TNF-
a
and -
b
, CSF,
erythropoietin, etc.)
Cytokine receptors
Phosphorylated target
proteins (e.g.,
STATs, or signal
transducers and
activators of
transcription)
4
Acetylcholine,
g
-aminobutyric
acid (GABA), excitatory
amino acids (glycine,
aspartate, glutamate, etc.)
Ligand-gated ion
channels
Changes in local
membrane potential
(e.g., depolarization)
cAMP, Ca
++
,IP
3
,
diacyglycerol,
cGMP
5
Acetylcholine, ACTH,
angiotensin,
catecholamines, FSH,
glucagon, histamine,
parathyroid hormones,
PGE
2,
serototin,
dopamine, etc.
G protein-coupled
receptors (GPCRs)
transmitted across the cell membrane to second messengers. This phenomenon is
principle evidently applies to signal transduction in the cell as postulated by the cell
language theory (Ji 1997a, b).
There are five well-established mechanisms effectuating transmembrane signal-
ing in living cells as summarized in Table
12.14
. All except Mechanism 1 are
mediated by receptors embedded in the cell membrane. Membrane receptors can be
viewed as
molecular machines
that perform three major biological functions:
1. The specific
recognition
of the cognate primary messengers
2. The
coupling
between first messengers and their intracellular counterparts, i.e.,
second messengers and
3. The
amplification
of the second messenger signals either directly by acting as a
kinase or an ion channel (see Mechanisms 2 and 4 in Table
12.14
) or indirectly
via another protein acting as a kinase (see Mechanisms 3 and 5)