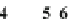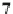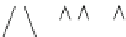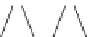Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 7.8 An example of a five-level temporal hierarchy composed of a set of coincidence-
detecting events (CDEs), each constructed from a set of three nodes, j-i-k, where the simultaneous
occurrence of events j and k leads, causes or correlates with event i
7.2.3 Enzymes as Building Blocks of the Temporal
Structures of the Cell
We can recognize two distinct kinds of hierarchies (or tree structures) in nature:
spatial
and
temporal
. The nodes of spatial hierarchies may be primarily associated
with
equilibrium structures
(equilibrons), whereas those of temporal hierarchies
The simplest
temporal hierarchy
is a set of n bifurcations, where n
¼
1 or greater.
When n
1, we have what may be called the “unit bifurcation.” A unit bifurcation
consists of three nodes connected thus: 1-2-3. When 1 and 3 are events whose
simultaneous occurrences (within a very short time window or time bin, say, m
seconds) leads to (or causes) event 2, we are dealing with what may be called the
“unit temporal bifurcation (UTB).”. This is equivalent to viewing 2 as a “coinci-
dence detector” or a “coincidence-detecting event (CDE).” We can easily imagine a
system of two or more CDEs coupled in such a manner as to form a tree, which may
be referred to as a
temporal hierarchy
(or
temporal web
).
We can represent a
temporal hierarchy
schematically as shown in Fig.
7.8
,
where the “leaves” (i.e., lowest elements 16 through 31) are inputs to a system
(to be defined below) observed at a given time slice, and the root of the hierarchy
(i.e., element 1) is the system output at that time point. We assume that the root
and the leaves are connected through a system of
coincidence detectors
, each
receiving two inputs (e.g., 8 and 9 at a given time point) within a short time gap,
D
¼
t, to produce one output (e.g., 4 at the same time point) when the combined
strength of the two inputs equals or exceeds a threshold value,
Y
(see Eq.
7.18
).