Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
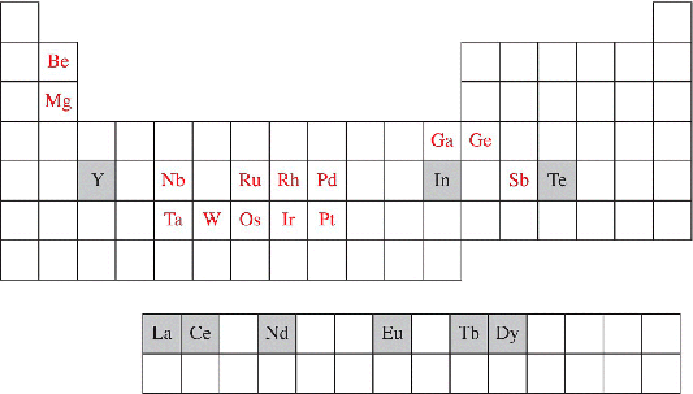
Ba, batteries; Cat, catalysts; E, electrical and electronic uses; P, photovoltaic.
With future shortages anticipated, a strategy for using these scarce
resources prudently and an aggressive plan to recover/recycle these are
needed. Inevitably, recovery and reuse of the higher-value materials will be
anattractivepropositions.WiththosematerialsbeyondHubbert'stypepeak
recycling will be the only way to ensure a continuing supply in the near
future. For instance, rhenium (Hubbert's peak in the late 1990s) is already
being extracted and recycled. In the West with an ingrained “disposable”
consumer culture, reuse-recycle will be a difficult task. But at some cost
point,itwillbecost-effectiveandevenbeverylucrativetorecyclethesethan
to be in short supply in the near future.
Figure 1.9
Critical elements likely to be in short supply in the near future.
The shaded boxes are those identified by the US DOE study (2010). The
others are additional critical elements identified by a European
Commission (2010).
1.2.4 Plastic Materials
Though commercially introduced into the market as a commodity material
some 60 years ago, the design versatility, low cost, formability, and