Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
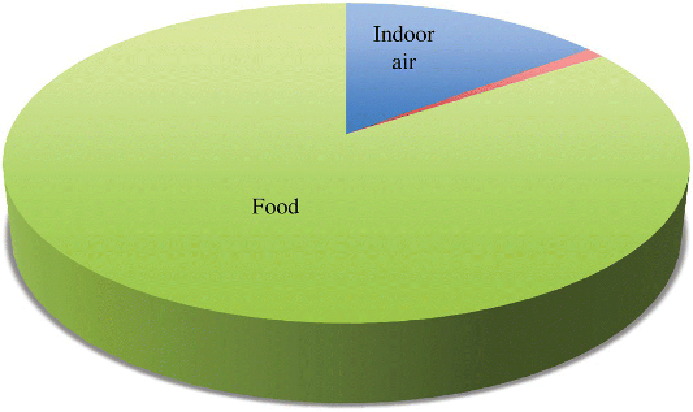
Figure 7.6
Intake of DEHP by source for an adult. Ingestion with food is
by far the most important mechanism of exposure.
Source: Reproduced with permission from Shea (2003).
Infants undergoing medical procedures may have additional exposure via
PVC tubing (e.g., IV tubing) (ATSDR, 2002), dialysis equipment (Center
for the Evaluation of Risks to Human Reproduction, 2006), or blood bags.
Adult exposure can also similarly occur through plastic medical devices
11
such as blood bags, PVC tubing (Koch et al., 2006) or personal care
products. Off-gassing from surfaces such as vinyl floor tiles and wallpaper
(Jaakkola and Knight, 2008) can also be a significant source of exposure.
Where exposure to multiple sources of phthalates are involved, the effect is
generally cumulative (Howdeshell et al., 2008).
In general, inhalation is not an important route of exposure to phthalates.
But volatilized phthalates in cabin air of automobiles can contribute
significantly to intake via inhalation exposure. A recent study on 23 vehicles
found DBP and DEHP at concentrations ranging from 1.96 to 3.66 µg/m
3
in the cabin air (Geiss et al., 2009). Cars parked outdoors can reach high
interior temperatures and correspondingly higher phthalate levels in the
air.Underworst-caseconditions,theconcentrationsofphthalatescanreach