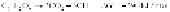Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6.4 BIODEGRADATION OF POLYMERS
The degradation of a substrate mediated by living organisms, usually
first attach on to the surface of a substrate, such as the plastic material,
as a biofilm (Lucas et al., 2008) and secrete exo-enzymes to break down
the plastic. As common polymers are water insoluble and have molecules
that are far too large to diffuse into the microbial cell, heterogeneous
biodegradation occurs outside the cell via the enzymes secreted by the
organisms. Any soluble products of biodegradation are low enough in
molecular weight to be absorbed or assimilated by the microorganisms.
Cellular metabolism of the sorbed nutrients yields as CO
2
and water,
liberating energy (stored as intracellular ATP) in the process.
Biodegradation can be either oxidative (aerobic) or reductive (anaerobic)
depending on the environment the polymer is placed in. In the latter case,
CH
4
, H
2
and sometimes NH
3
are formed as by-products of the degradation.
Forglucose,thebiodegradationreactioncanbesummarizedinthefollowing
reactions.
Aerobic biodegradation:
Anaerobic biodegradation:
There is net energy gain to the microorganism from biodegradation and
they utilize the derived energy for their growth and reproduction. Growth
incorporates some of the carbon from the biodegraded polymer into new
biomass. In common with other reactions, biodegradation is also
accelerated at higher temperatures and also requires a minimal level of
moisture. The latter is essential for the microbial consortia to exist and is
a schematic diagram of the environmental degradation of plastics material.
It is important to appreciate that a polymer that is readily biodegradable
under aerobic exposure (such as poly(e-caprolactone) or PCL) need not be
necessarily biodegradable under anaerobic conditions (Mohee et al., 2008).