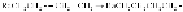Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Termination
by combination of macromolecular radicals
The overall reaction is summarized as follows:
3.3.2 Condensation or Step Growth Reaction
Condensation reaction is one where two monomers or short functional
macromolecule segments combine together to form a long segment, usually
with the elimination of a small molecule such as water or alcohol. For this to
takeplace,eachreactingsegmentmusthavechemicallyreactiveendgroups.
The reaction of a pair of such difunctional molecules or oligomers yields a
polymer by step growth process and is illustrated schematically below:
The reaction between a diamine and a dicarboxylic acid to yield a polyamide
(or a nylon) is an example of a polycondensation. The basic reaction is
shown below. The reaction does not stop here as the product too has the
same functional groups and can therefore react with other products to yield
chains of different lengths. In this type of reaction, all molecular species
such as monomers, dimers, trimers, and longer chains can react
concurrently, yielding chains with high enough
Mw
values that would make
the polymer practically useful: