Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
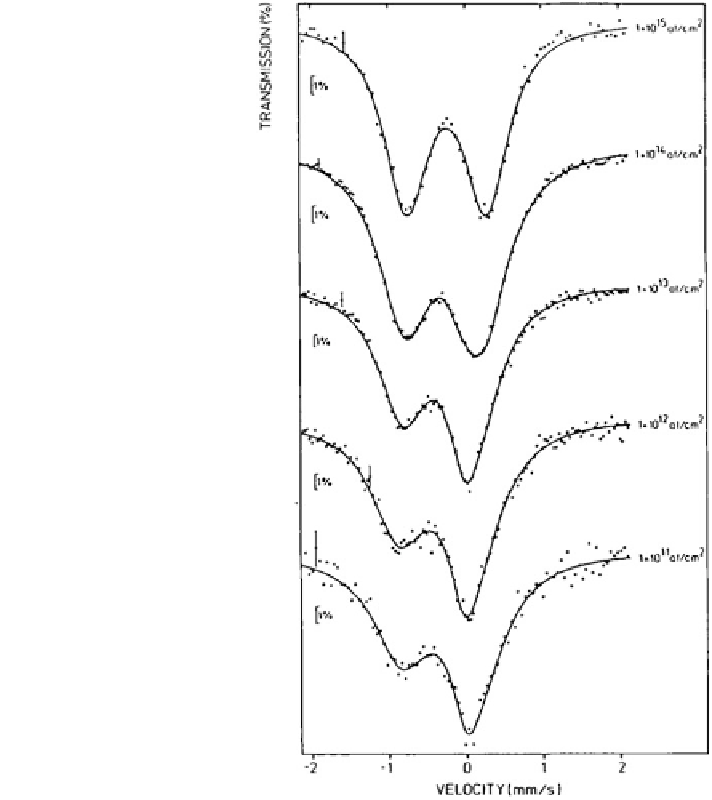
Fig. 6.10
57
Co/
57
Fe
Mössbauer spectra as a
function of ion implantation
fluence [
21
]
interstitial Fe in Si. The spectra, shown in Fig.
6.12
, were interpreted as composed
of the ''amorphous'' doublet and a superimposed single line (with isomer shift
d =?0.84(1) mm/s with respect to a-Fe).
Due to the improved statistics, an increase in the linewidth of this single line
could be observed for higher target temperatures. This line broadening was ana-
lyzed in terms of a diffusional motion of the iron atoms, which are able to make
atomic jumps within the lifetime of the excited nuclear state. Diffusion coefficients
were derived (Fig.
6.13
) from the broadening of the Mössbauer lines, and these
were found to be remarkably consistent with the known high- and low-temperature
diffusion coefficients of Fe in Si.
For the ''amorphous'' site (isomer shift d =?0.20(3) mm/s, quadrupole split-
ting D = 0.95(5) mm/s) no microscopic model exists up to today. It is dominant in