Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
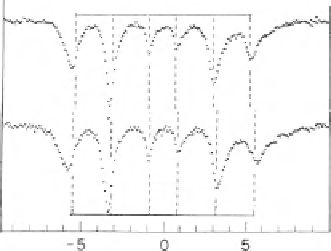
Fig. 5.8
57
Fe Mössbauer
absorption spectra for MgO-
coated Fe surface at RT and
4 K. The peak positions of
bulk a-Fe are indicated for
comparison [
25
]
RT
4K
Velocity (mm/s)
importance of studies on interfaces between ferromagnetic metals and tunneling
barriers (insulators) has been closed up.
Mössbauer spectroscopic studies on Fe metal surfaces covered by non-metallic
materials have been carried out using interface-selectively enriched absorber
samples. Spectra for MgO-covered Fe surface are shown in Fig.
5.8
.
The spectra indicate that the interface Fe layers are entirely ferromagnetic and
oxidized fraction or non-magnetic fraction is not observable. The line shapes of each
peak are asymmetric and the tailing to outside is observed. This result means that the
hyperfine field is distributed towards larger values than the bulk, which indicates that
the hyperfine field at the interface layer is larger than the standard bulk value.
Therefore it is suggested that the local magnetic moment of Fe at the topmost
interface layer is enhanced by the interface effect. A large magnetic moment of
interface layer is a favorable condition to hold a tunneling spin current with a high
polarization, which is a key to realize a large TMR effect. This result seems to be
consistent with the recently reported very large TMR effect in Fe/MgO/Fe system.
On the other hand, Mössbauer measurements on very thin Fe layer sandwiched in
Al
2
O
3
layers had exhibited a significant amount of non-magnetic fraction, sug-
gesting that Al
2
O
3
-coated Fe surface tends to loose ferromagnetic moments [
13
].
The reason why Al
2
O
3
is not an appropriate tunneling barrier material seems to be
the interface magnetic effect of Fe layer covered by Al
2
O
3
. However, both
Mössbauer measurements on MgO-coated and A
2
O
3
-coated Fe interfaces, intro-
duced here, were old works, which had been carried out before the discovery of large
TMR effect. More refined studies on Fe interfaces contacting with insulating
materials are to be attempted in relation to TMR phenomena.
5.4.3 Interfaces of Fe-Oxides
Magnetic behaviors of surfaces and interfaces in non-metallic materials also are
very interesting subjects as well as those in metallic thin films. In contrast to
metallic cases, local magnetic moments at the top surface layer in non-metallic
systems are not much influenced but surface anomaly should appear in the