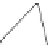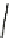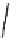Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
-
F
Fe
3+
b
c
a
O
F
Fe
3+
w
c
b
a
Al+3
F
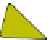
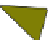
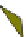
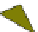
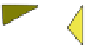
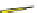
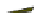
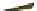
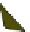
Fig. 4.21
Crystalline
(left)
and
magnetic
structures
(right)
of
rhombohedral
r-FeF
3
(top),
hexagonal tungsten bronze HTB-FeF
3
(middle) and pyrochlore pyr-FeF
3
(bottom)
the HTB planes which are antiferromagnetically coupled; the pyrochlore form of
FeF
3
orders below 20 K with 4 ferromagnetic sublattices oriented at 109 from each
other. Both the non collinear magnetic structures and the reduction of magnetic
ordering temperatures are attributed to the frustration of the antiferromagnetic
exchange interactions implied by the cationic topology. The amorphous ferric
fluoride varieties can be prepared by either vapour quenching onto a cold substrate or
fluorination route [
163
]. They behave as a speromagnet below the freezing tem-
perature estimated at about 30 K can be thus structurally described from a dense
random packing of corner-shared octahedral units [
162
-
164
].
The rhombohedral form was ground under Ar atmosphere to prepare nanostructured
powders with milling conditions as reported in X and sampling was highly controlled
because of the high hygroscopic character of fluoride powder [
165
]. As illustrated in
Fig.
4.22
, the X-ray pattern of the ground ferric fluoride powder exhibits high statistics
and is expressed with a square root coordinate scale in order to better visualize the low