Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
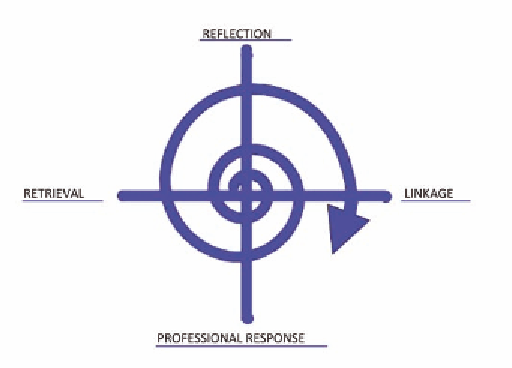
Figure 3. Human computer interaction spiral (Martin, McKay & Hawkins, 2006)
studies due to not having access to an adequate
personal computer, the Internet and other technolo-
gies. An informed approach to educational design
is required that integrates personal reflection,
theory and practice.
the inclusion of “multidisciplinary” knowledge.
The HCI Spiral is presented in Figure 3.
The application of the HCI spiral requires
four steps. The factual elements of a situation are
retrieved and reflected upon. This includes reflec-
tion on personal assumptions, attitudes and values
as well as consideration of power relationships
and possible discrimination according to; class,
culture, ability, health, gender, age, spirituality and
sexuality. This is followed by linkage with theory
that can account for, or explain, the information
retrieved and personal reflections. This in turn
leads to the final step, an informed professional
response. The cycle continues as new informa-
tion is retrieved. The spiral is as an important
element of the design with an upward spiral
reflecting the progress achieved through design,
re-design and continual improvement processes.
However, the spiral may go up or down rapidly
or slowly depending upon the responsiveness of
the design team.
In applying this model to education, it is es-
sential to differentiate between the type of learning
and the technological means that bring forward an
effective online instructional architecture to sup-
port it. This necessitates a close look at the type
of learning activities that are required to prepare
knoWleDge Development:
tHe Human computer
interaction Spiral
It can be difficult establishing meaningful links
between theory and practice within a discipline
with this becoming more complex when theoreti-
cal concepts from the disciplines of instructional
design and education are also included. A key
consideration is how to give theory operational
meaning. Bogo and Vayda (1987) adapted the
work of Kolb (1984) on experiential learning
to social work education developing what they
termed the “Integration of Theory and Practice
Loop” (ITP Loop).As reported elsewhere (Martin,
McKay & Hawkins, 2006) this model has been
further developed into the “the Human Computer
Interaction Spiral (HCI Spiral)” and applied more
broadly to the multidisciplinary context of the
human services. Another feature of this model is
Search WWH ::

Custom Search