Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
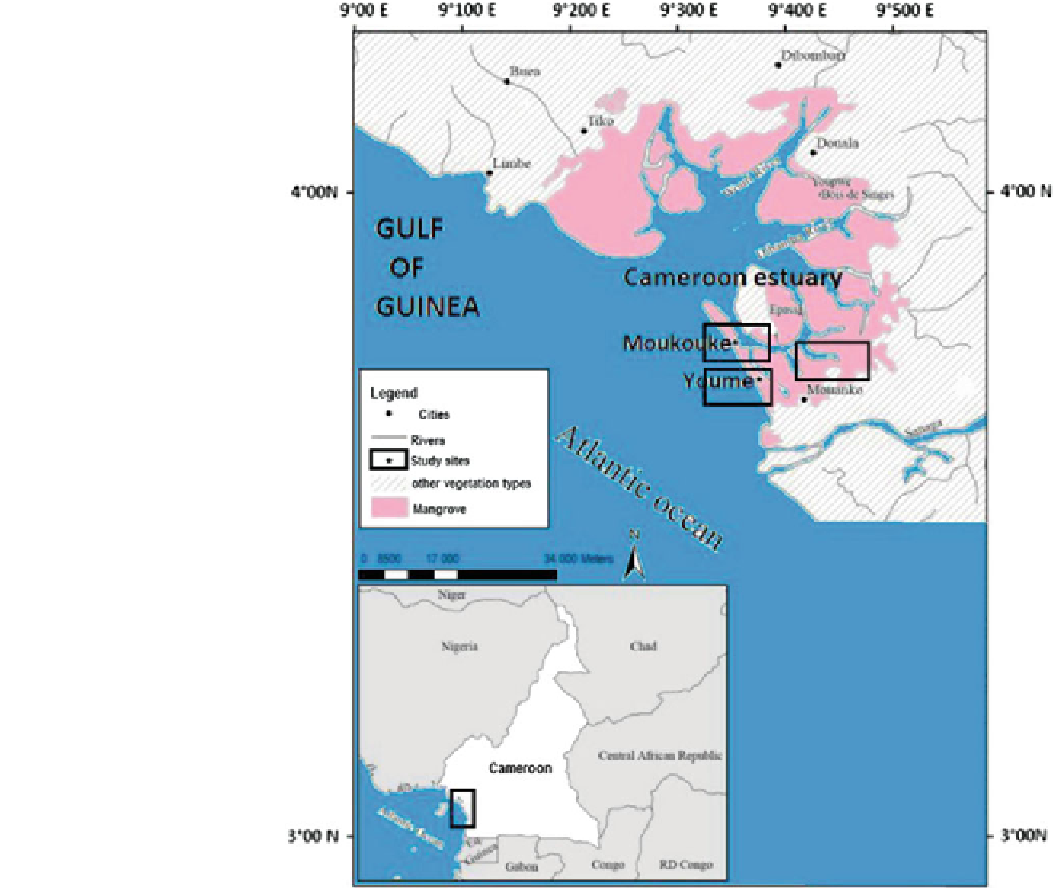
Fig. 2
Map showing the
sampling stations at Douala-Edea
reserve in Cameroon estuary
The Reserve is limited in the North by the rivers Wouri
and Dibamba; the East by rivers Sanaga, Dipombe and
Kwakwa; the South by river Nyong; and the West by the
Atlantic Ocean for some 100 km coastline from river Nyong
to the Cameroon Estuary. The climate is equatorial type
characterized by abundant rain (3,000-4,000 mm) and gen-
erally high temperatures with monthly average of 24-29 C
with a dry season spanning from November to March.
ecosystems were evaluated and identified based upon their
main plant species (Rhizophora racemosa, Avicennia ger-
minans) and their stability (very little degradation). Three
study sites were then identified, based on the type of man-
grove ecosystem vegetation: (1) pure red mangroves (R.
racemosa); (2) pure white mangroves (A. germinans); and (3)
mixed stand (red and white mangroves). These two reserves
in both countries were selected for investigation because the
mangrove ecosystems are relatively well conserved.
Study Site Selection
A preliminary survey was conducted in all of the existing
mangrove ecosystems in the Ada estuary complex in the
Greater Accra region in Ghana and in the Cameroon estuary
(Douala-Edea Reserve) in Cameroon. These zones in both
countries are all protected areas and among the largest
reserves, with a relatively high mangrove cover (Spalding
et al.
2010
; Ramsar-MAVA-UNEP
2012
). The mangrove
Selection and layout of plots
Combinations of sampling approaches were used to achieve
a nested design. Targeted sampling (TS) method was used to
select areas of species agglomerations where three study
sites, representing the various species agglomerations (stands
of pure Rhizophora, pure Avicennia and a mixture of them in
equal proportion), were retained (Fig.
3
). This was followed
by a three-stage sampling approach to subdivide the plots
Search WWH ::

Custom Search