Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
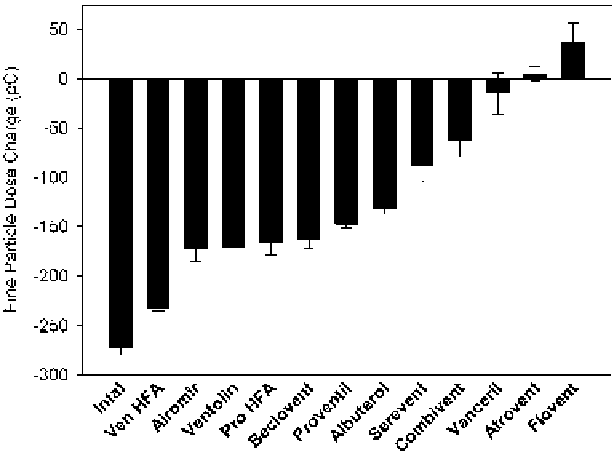
Fig. 3.3
Intrinsic electrostatic charge series for different MDI products (
From
[
36
]—
used with
permission
)
evaporation rate caused by interaction of water vapor with the surfaces of the evapo-
rating droplets. However, such extreme conditions are unlikely to be encountered in
testing laboratories with basic heating ventilation and air conditioning controls in
place for the building.
Electrostatic charge associated with triboelectrification of the metered-dose con-
tents as they emerge from the metering valve and are atomized results in intrinsic
charge associated with the aerosol that is different from one product to another
(Fig.
3.3
) [
36
]. The charge associated with fine particles (fine particle dose in
Fig.
3.3
) depends on many factors including the formulation itself, as well as the
materials used for the metering valve system. This intrinsic charge combined with
the presence of surface charge associated with the inhaler mouthpiece or add-on
device that may be present is a major source of APSD variability [
37
] and must be
mitigated or better eliminated altogether, for reproducible results to be obtained in
cascade impactor-based measurements [
38
].
3.3.1.3
Nebulizing Systems and Soft Mist Inhalers
Nebulizing systems and SMIs operate on the basis of atomization of a liquid (usu-
ally an aqueous solution or suspension of the API in physiologically normal saline)
by various methods, including pneumatic pressure, ultrasonics, and mechanical
pressure through ultrafine orifices (SMIs), or by applying vibration of the bulk
Search WWH ::

Custom Search