Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
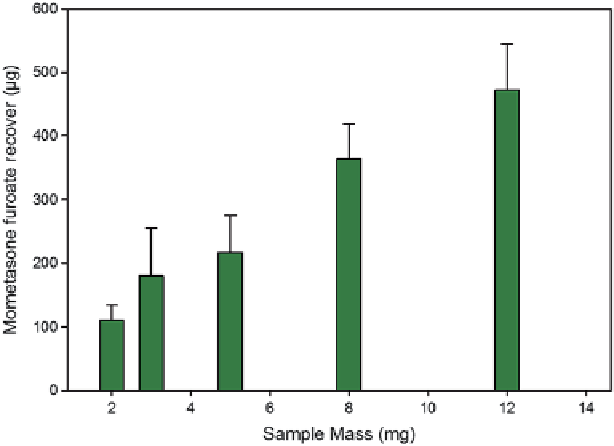
Fig. 10.69
FPM
<ca.6.5μm
of mometasone furoate [
n
= 5 replicates at each condition (mean ± SD)]
delivered to the short stack ACI over a range of sample weights which, with a 12 mg sample load
(15% blend mometasone furoate), will deliver approximately 500
μ
g to the filter stage (
From
[
60
]—
used with permission
)
the current status of the measurement technology was established and following
issues were identified [
62
]:
1. Measurements made by AIM-based equipment for pMDIs and nebulizers pro-
vide measures of fine particle fraction that are in substantial agreement with the
equivalent metric from the corresponding full-resolution impactor (either the
ACI or NGI).
2. Measures of
FPF
by FSI were frequently higher than the corresponding full-
resolution data for DPI testing. In contrast with the evaluation of pMDIs and
nebulizers, where the impactor is operated at a fixed flow rate throughout the
determination, the DPI test is more complex in that the flow rate at initiation of
the measurement is zero and rapidly rises to a stable value as the pressure field
within the DPI and measurement system stabilizes. Two possible causes were
identified that need further investigation:
a. The start-up kinetics of both abbreviated and full-resolution impactor systems
appear to be important, since the compendial method necessitates initiating
flow from the DPI at the start of measurement, so that the flow through the
system is developing during the initial few hundred milliseconds of the
determination.
b. Differences in sharpness of cut for the insert in the FSI compared with both
NGI and perhaps more so with the ACI whose stage collection efficiency
curves are noticeably less steep than those of the NGI may also be responsible
Search WWH ::

Custom Search