Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
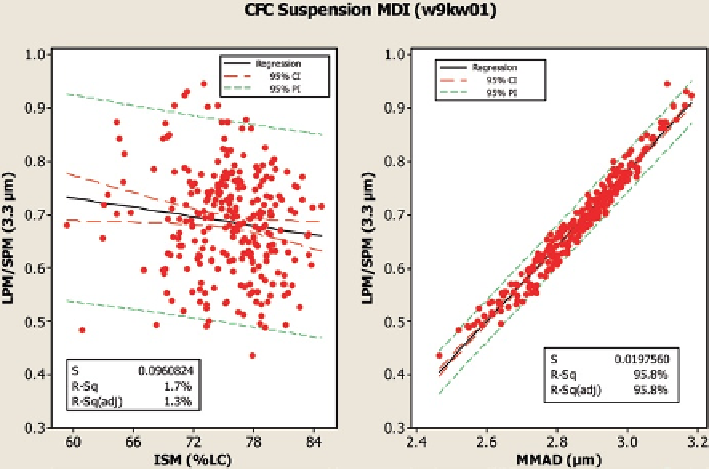
Fig. 7.10
Example regression plots for
LPM/SPM
ratio versus
ISM
and
MMAD
(OIP
w9kw01
,
CFC Suspension MDI) (
From
[
11
]—
used with permission
)
References
1. Newman SP, Chan H-K (2008) In vitro/in vivo comparisons in pulmonary drug delivery.
J Aerosol Med 21(1):1-8
2. Heyder J, Svartengren MU (2002) Basic principles of particle behavior in the human respira-
tory tract. In: Bisgaard H, O'Callaghan C, Smaldone GC (eds) Drug delivery to the lung.
Marcel Dekker, New York
3. Dolovich M (2002) Airway delivery devices and airways/lung deposition. In: Schleimer R,
O'Byrne PM, Szefler S, Brattsand R (eds) Inhaled steroids in asthma. Marcel Dekker, New
York, NY, pp 169-212
4. Usmani OS, Biddiscombe MF, Nightingale JA, Underwood SR, Barnes PJ (2003) Effects of
bronchodilator particle size in asthmatic patients using monodisperse aerosols. J Appl Physiol
95:2106-2112
5. Usmani OS, Biddiscombe MF, Barnes PJ (2005) Regional lung deposition and bronchodilator
response as a function of β2-agonist particle size. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172(12):
1497-1504
6. Zanen P, Go LT, Lammers JWJ (1994) The optimal particle size for beta-adrenergic aerosols
in mild asthmatics. Int J Pharm 107:211-217
7. Zanen P, Go LT, Lammers JWJ (1995) The optimal particle size for parasympathicolytic aero-
sols in mild asthmatics. Int J Pharm 114:111-115
8. Zanen P, Go LT, Lammers JWJ (1996) Optimal particle size for beta-agonist and anticholiner-
gic aerosols in patients with severe airflow limitation. Thorax 51:977-980
9. Newman SP (1998) How well do in vitro particle size measurements predict drug delivery
in vivo? J Aerosol Med 11(S1):S97-S104
Search WWH ::

Custom Search