Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
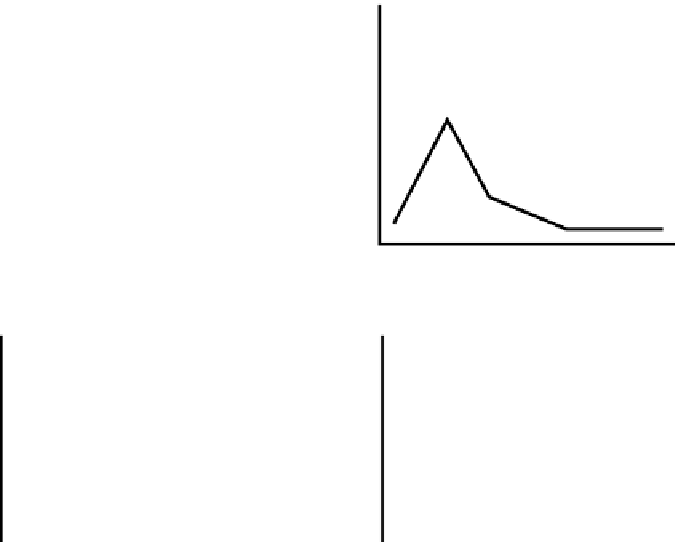
lower
size
limit
upper
size
limit
lower
size
limit
upper
size
limit
aerodynamic diameter (
m
m)
aerodynamic diameter (
m
m)
Nominal APSD
Change in Area
lower
size
limit
upper
size
limit
lower
size
limit
upper
size
limit
aerodynamic diameter (
m
m)
aerodynamic diameter (
m
m)
Change in Mean
Change in Mean & Area
Fig. 7.6
Possible variation types in a unimodal OIP APSD
The ratio metric, large to small particle mass (
LPM
/
SPM
) is highly correlated with
the mass-weighted mean of the APSD (represented customarily by its
MMAD
), but
ond metric, impactor-sized mass (
ISM
) is related to the area defined by the APSD
when expressed in differential mass-weighted format, but independent of the
mean of the distribution [
11
]. Both metrics can be readily obtained directly either
from full resolution or abbreviated CI measurements (the latter is discussed in
In order to characterize the performance of EDA, the CI-WG has utilized CI data
from marketed OIPs previously gathered by the parent IPAC-RS organization into a
blinded database, employing two fundamental statistical approaches in its assess-
ment: measurement system analysis (MSA) and operating characteristic curves
(OCCs). Background information on measurement processes and these two statisti-
cal approaches is provided here in order to aid the reader in understanding the theo-
retical principles that underlie EDA, before assessing the subsequent material that is
presented in Chap.
8
.










Search WWH ::

Custom Search